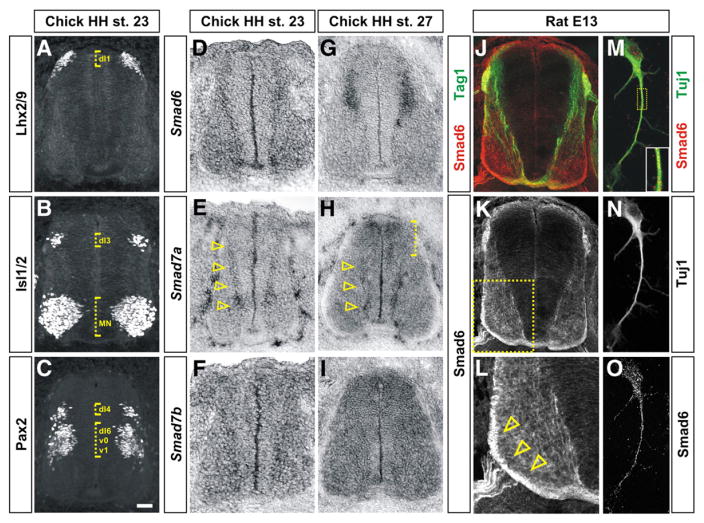
Fig. 1.
Inhibitory Smads have dynamic expression patterns during early spinal cord development. (A–C) Transverse sections of the spinal cord taken from HH stage 23 chicken embryos labeled with antibodies against Lhx2/9 (A), Isl1/2 (B) and Pax2 (C) to establish the positions of dI1, dI3 and dI4 populations of dorsal interneurons (dotted brackets). (D–I) In situ hybridization experiments for Smad6 (D and G), Smad7a (E and H) and Smad7b (F and I) on sections of the spinal cord taken from either HH stage 23 (D, E and F) or HH stage 27 (G, H and I) chicken embryos. (D and G) Although Smad6 is broadly expressed in post-mitotic spinal neurons at HH stage 23, expression resolves to dorsal post-mitotic neurons by HH stage 27. (E and H) Smad7a is expressed at the highest levels in differentiating spinal neurons in the intermediate and ventral spinal cord at both HH stages 23 and 27 (arrowheads). At HH stage 27, Smad7a is also expressed in dorsal neural progenitors (dotted bracket, H). (F and I) Smad7b is expressed throughout the spinal cord with the highest levels at HH stage 27. (J–O) Antibodies against Smad6 (red, J–M and O) label neural processes in transverse sections (J–L) and Tuj1+ (green, M and N) dissociated dorsal neurons (M–O) taken from E13 rat spinal cords. Smad6 is co-expressed in the Tag1+ (green) dI1 (commissural) axons in the dorsal spinal cord (J) and is present at the highest levels on the contralaterally projecting commissural axons (compare arrowheads in L to the arrowhead in Supplemental Fig. 4B). Panel L is a higher magnification view of the boxed region in K. Scale bar: A–L: 25 μm, M–O: 5 μm.