Figure 5. A decreased level of Hmga1, an IMP2 client mRNA, causes the upregulation of IGFBP2 and Grb14 abundance and the slowed proliferation of IMP2 deficient MEFs and RD cells.
(A) IMP2 binds Hmga1 mRNA. IPs were prepared from extracts of Imp2+⁄+ and Imp−⁄− MEFs (left pair) and from RD cells (right pair) with anti-IMP2 antibody (black) or nonimmune IgG (orange). The relative enrichment of HMGA1 mRNA in each IP is quantified by real time RT-PCR. (B) Hmga1 mRNA abundance in Imp2+/+ and Imp2−/− MEFs. RNA was extracted from Imp2+/+ and Imp2−/− MEFs and the abundance of HMGA1 mRNA was determined by QPCR. The abundance in Imp2−/− MEFs relative to Imp2+/+ MEFs (set to 1.0, black bars) is shown in the red bar. (C) The turnover of Hmga1 mRNAs in Imp2+/+ and Imp2−/− MEFs. The t1/2 of Hmga1 mRNA turnover was determined as in Figure 3B. (D) The percentage of Hmga1mRNAs residing in polysomes in Imp2+/+ and Imp2−/− MEFs. Determined as in Figure 3C. (E) The turnover of the HMGA1 polypeptides in Imp2+/+ and Imp2−/− MEFs. The t1/2 of HMGA1 polypeptide turnover determined as in Figure 3D. (F) The abundance of the HMGA1polypeptides in Imp2+/+ and Imp2−/− MEFs. The relative abundance of HMGA1was determined by quantitation of extract immunoblots. Values determined by MS are found in Supplementary file 2. For Figure 5B–F, +p<0.05, *p<0.01 vs Imp2+/+. (G) IGFBP2 mRNA is regulated by the abundance of HMGA1 polypeptide. IGFBP2 mRNA in RD cells and Imp2+/+ MEFs stably expressing doxycycline-inducible shRNAs against HMGA1 (left set) or doxycycline-inducible HMGA1 cDNAs (right set). Doxycycline = colored bars; DMSO = black bars. (H) HMGA1 binds the Igfbp2 but not the Grb14 promoter. MEFs (~10 million) were washed and protein was cross-linked to DNA using formaldehyde. ChIP was performed as described in Methods using antibodies to HMGA1 (black) or nonimmune IgG (red). (I) Both IGFBP2 and Grb14 protein levels are regulated by HMGA1 polypeptide abundance. Immunoblots were performed using MEFs extracted 72 hr after doxycycline induction of Hmga1 shRNA (left) or induction of HMGA1 cDNA expression (right). (J) HMGA1 overexpression restores the proliferation of Imp2−/− MEFs close to that of the similarly treated Imp2+/+ MEFs. Parental MEFs or MEFs stably expressing a doxycycline-inducible HMGA1 overexpressing MEF cells were treated with doxycycline and cell number was measured daily. The bar graphs were calculated as in Figure 2E. (K) The HMGA1 overexpression restores the proliferation of IMP2 CRISPR RD cells nearly identical to similarly treated parental RD cells. As in Figure 5J.
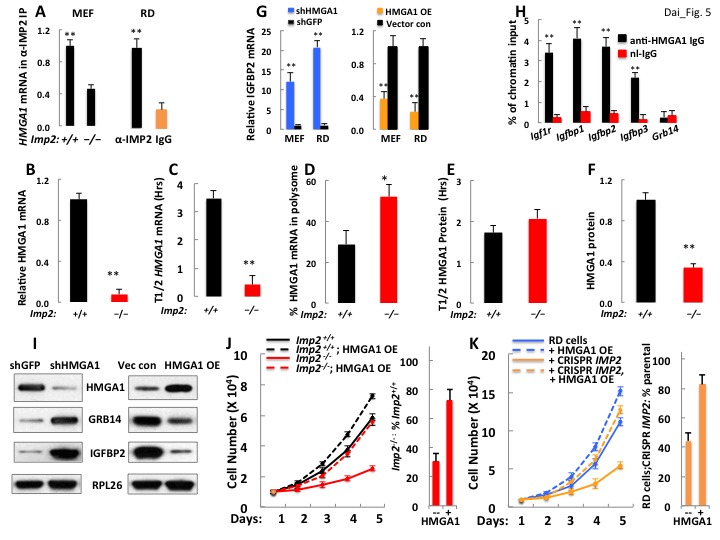
Figure 5—figure supplement 1. RNAseq indicates that IMP2 binds HMGA1 mRNA predominantly at the 3’UTR.

Figure 5—figure supplement 2. Depletion of IGFBP2 does not affect the abundance of Grb14.
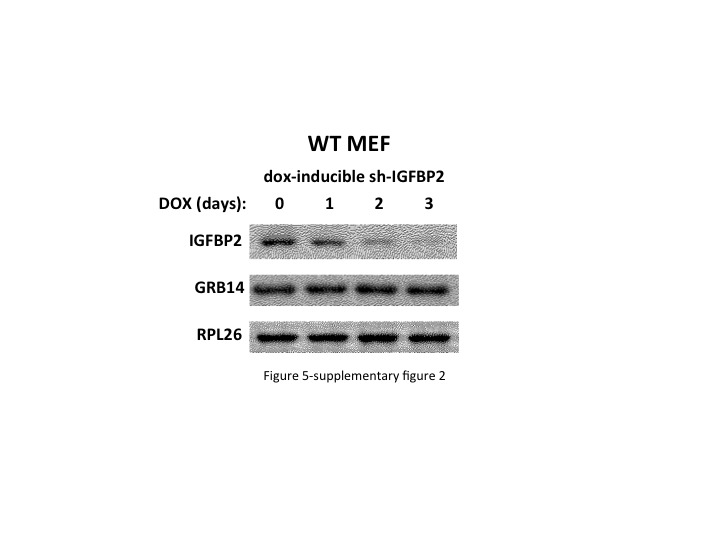
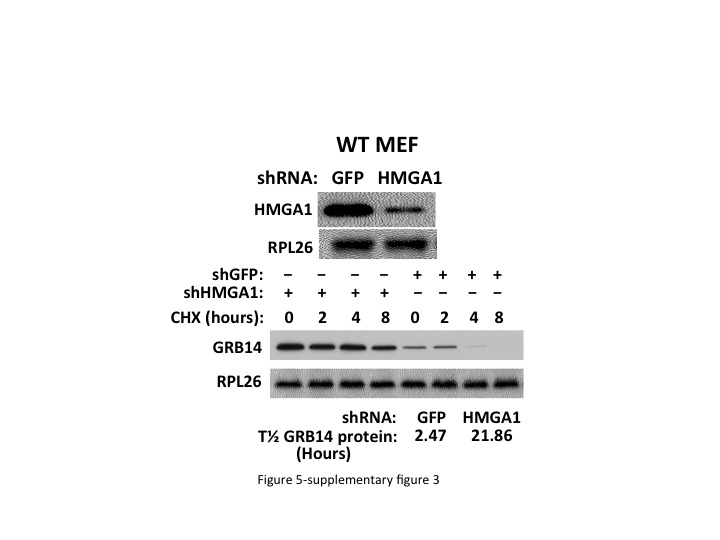
Figure 5—figure supplement 3. Depletion of HMGA1 prolongs the half-life of the Grb14 polypeptide.