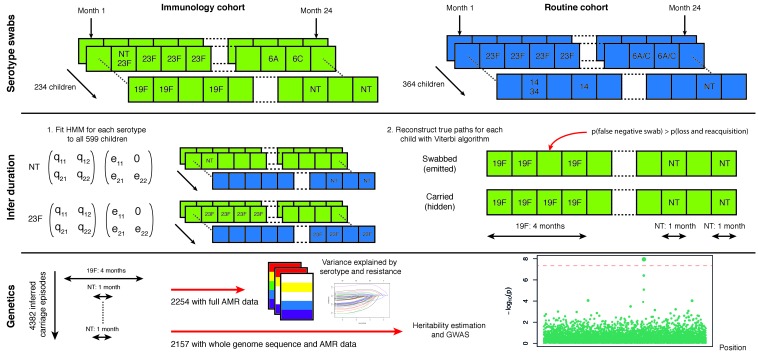
Figure 1. Swabbing and sequencing study design.
We start with serotype swab data on 598 children from two cohorts, taken every month after birth for two years. For all samples we fitted the transition and emission probabilities of a continuous time hidden Markov model for each serotype. Then, for each child, we used these parameters were then used to infer the most likely carriage durations. We matched carriage episodes with resistance and genomic data for 2157 episodes to draw conclusions on the basis of variation in this epidemiological parameter.