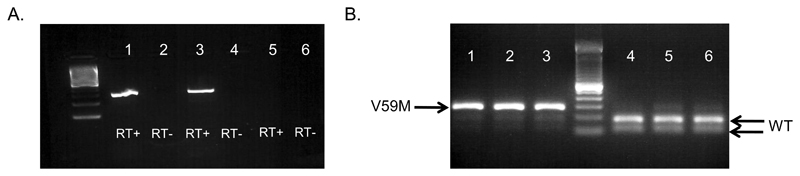
Figure 1. Kir6.2 expression in adult nV59M mice.
(A) Identical RNA aliquots of brain tissue from control (lanes 1-2) or nV59M (lanes 3-4) mice were processed in a reverse transcription reaction with reverse transcriptase included (RT+) or omitted (RT-). Amplification of the Kir6.2 transcript was only seen in RT+ samples, indicating there was little genomic DNA contaminating the RNA samples. Lanes 5-6 are nuclease-free water controls. (B) Kir6.2 RNA expression in brain tissue isolated from nV59M (lanes 1-3) or control (lanes 4-6) mice. Wild-type (WT), but not mutant (V59M), Kir6.2 cDNA was digested by restriction enzyme BtsCI, hence two bands indicates the presence of WT Kir6.2 only while three bands indicates both WT and V59M mutant Kir6.2 are present. Data are representative of experiments on 5 control and 5 nV59M mice.