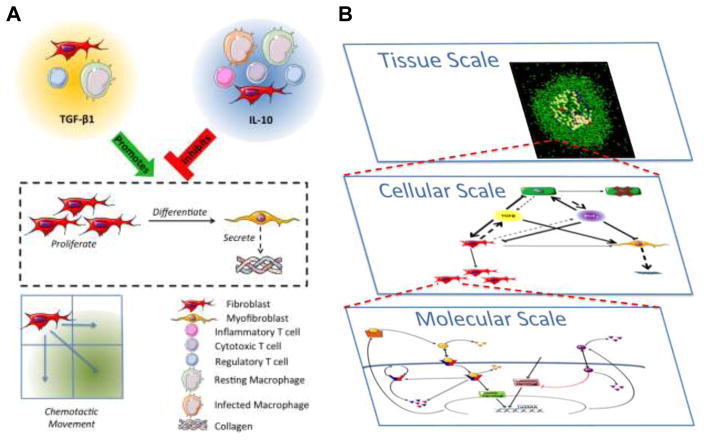
Figure 2. Fibroblast dynamics within hybrid multi-scale model architecture.
A) Cellular and molecular scale interactions of fibroblasts in the hybrid multi-scale computational model. Fibroblasts, regulatory T cells, and resting macrophages secrete TGF-β1. Fibroblasts, resting and infected macrophages, and all T cell types secrete IL10. Fibroblast to myofibroblast differentiation, as well as myofibroblast secretion of collagen, are promoted by TGF-β1 and inhibited by IL-10. Fibroblasts migrate in response to granuloma associated chemokine milieu. Agent based model rules are available at: http://malthus.micro.med.umich.edu/GranSim/. B) Individual scale models are combined to create a single hybrid multi-scale model of lung granuloma formation and function. The molecular scale includes TGF-β1 receptor ligand signaling dynamics within a single fibroblast, cytokine secretion and diffusion within the environment. At the cellular scale, individual agents, including macrophages, T cells, and fibroblasts, respond based on probabilistic rules to stimuli and cytokines within their local environment. The dynamics from Panel A are included within this scale. At the tissue scale we observe emergent behavior that can be characterized and compared to experimental data.