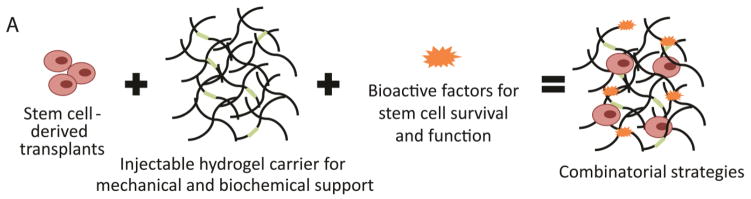
Figure 1. Design of injectable hydrogel delivery platforms for improved stem cell-derived therapeutics.
A) Combinatorial regenerative medicine strategies often include encapsulation of stem cell-derived transplants within injectable hydrogels designed to provide cell appropriate mechanical support and biochemical cues along with co-encapsulation of bioactive factors. B) The design of injectable hydrogels must consider four separate phases of hydrogel use. In the first and second, some injectable hydrogels can protect cells during the potentially harmful pre-injection and injection processes, which exposes cells to a variety of crosslinking mechanisms and mechanical forces. Third, some injectable hydrogels can improve acute cell survival and functionality by providing appropriate mechanical and biochemical matrix cues along with soluble bioactive factors. Fourth, carefully developed injectable materials can promote grafted cell function within host tissue as it degrades.