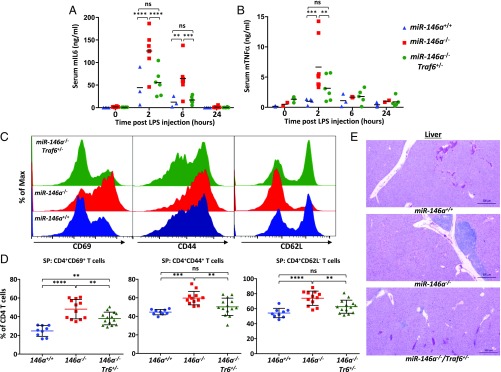
Fig. 3.
Lowering the Traf6 gene dose rescues aberrant inflammation phenotype in miR-146a–null mice. (A and B) Normal cytokine response to bacterial endotoxin challenge in miR-146a−/−Traf6+/− mice. Serum levels of IL-6 (A) and TNF-α (B) cytokines in miR-146+/+ (n ≥ 3), miR-146a−/− (n = 6), and miR-146a−/−Traf6+/− (n = 6) mice challenged intraperitoneally with a sublethal LPS (1 mg/kg) dose. Peripheral blood was collected at the indicated time points and cytokine concentrations were analyzed in the serum by sandwich ELISA. All mice were female and aged 3–4 mo. (C and D) Traf6 haploinsufficiency reverts the hyperactivated state of peripheral miR-146a−/− T cells. (C) FACS analysis of CD69, CD44, and CD62L activation markers on CD4+ T cells isolated from miR-146+/+ (blue plots), miR-146a−/− (red plots), and miR-146a−/−Traf6+/− (green plots) spleens. (D) Quantification of CD69, CD44, and CD62L expression levels on CD4+ T cells isolated from miR-146+/+, miR-146a−/−, and miR-146a−/−Traf6+/− spleens (n > 9 animals for all genotypes, female mice aged 9–10 mo). Values are reported as percent of CD4+ T cells. (E) Lowering the Traf6 gene dose in miR-146a−/− mice decreases lymphohistiocytic infiltrates in liver. Representative H&E-stained sections from 9- to 10-mo-old miR-146+/+, miR-146a−/−, miR-146a−/−Traf6+/− mice. Data are shown as mean ± SD. P values were calculated using either standard one-way or two-way ANOVA tests. **P ≤ 0.01; ***P ≤ 0.001; ****P ≤ 0.0001; ns, not significant; SP, spleen. (Magnification: 20×.)