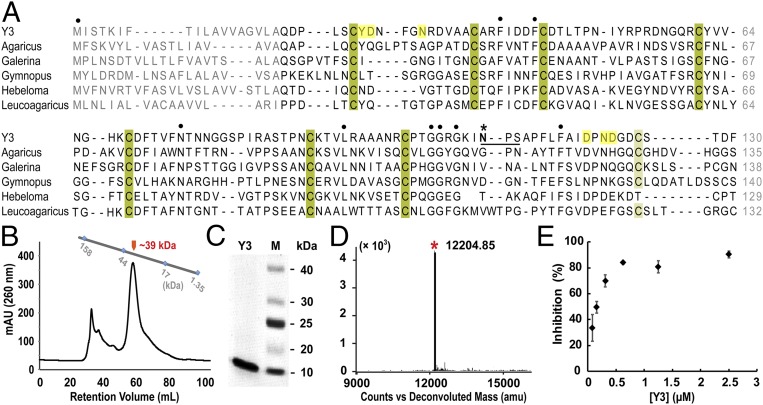
Fig. 1.
Biochemical characterization of Y3. (A) Sequence alignment of Y3 and its homologs from fungal species. Conserved cysteine residues that potentially form disulfide bridges are shaded in dark- and light green and all other conserved residues are indicated with dots (·). Potential N-glycosylation site (Asn110-Ser112) in Y3 is underlined with a dark line, and Asn110 is labeled with an asterisk (*). Residues potentially involved in ligand binding are shaded in yellow. Y3: C. comatus, GenBank: ADK35888.1; Agaricus: Agaricus bisporus var. burnettii JB137-S8, GenBank: XP_007333380.1; Galerina: Galerina marginata CBS 339.88, GenBank: KDR84548.1; Gymnopus: Gymnopus luxurians FD-317 M1, GenBank: KIK60251.1; Hebeloma: Hebeloma cylindrosporum h7, GenBank: KIM42673.1; Leucoagaricus: Leucoagaricus sp. SymC.cos, GenBank: KXN92904.1. (B) Recombinant Y3 was a putative dimer as shown in SEC analysis. Retention volumes of molecular standards of 1.35, 17, 44, and 158 kDa are indicated. (C) SDS/PAGE analysis showed the high purity of recombinant Y3. (D) The m/z value of purified Y3 at 12,204.85 in MALDI-MS analysis matched with calculated molecular weight of mature Y3 monomer (12,229.54 Da). (E) The inhibitory curve of recombinant Y3 on TMGMV infection. Data are presented as mean ± SD (n = 6).