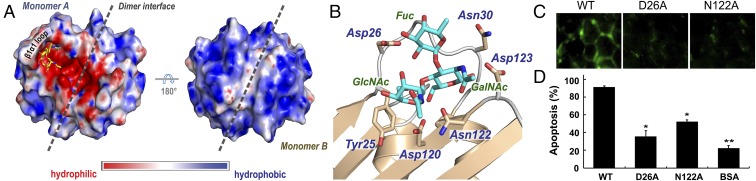
Fig. 5.
Y3 contained a large pocket for interacting with LDNF primarily through H-bonding network. (A) The putative glycan binding pocket of Y3. Left, an electrostatic surface representation of the Y3 dimer. The LDNF motif was modeled into the Y3 dimer and aligned along with the β1α1 loop. Hydrophilic and hydrophobic regions are shown with red and blue, respectively. Right, the dimer rotated by 180° to show the hydrophobic face. (B) A close-up view of the binding site with the docked LDNF. Key residues involved in H-bond interactions are labeled. (C) Fluorescence microscopy images of Jurkat cells after treatment with FITC-labeled Y3, Y3D26A, and Y3N122A. (D) Annexin V/7-AAD apoptotic assays revealed significantly decreased anti-Jurkat activity of Y3D26A and N122A mutants (1 µM). Data are presented as means ± SD (n = 3). Significant differences between WT and mutants are shown (*P < 0.05; **P < 0.01).