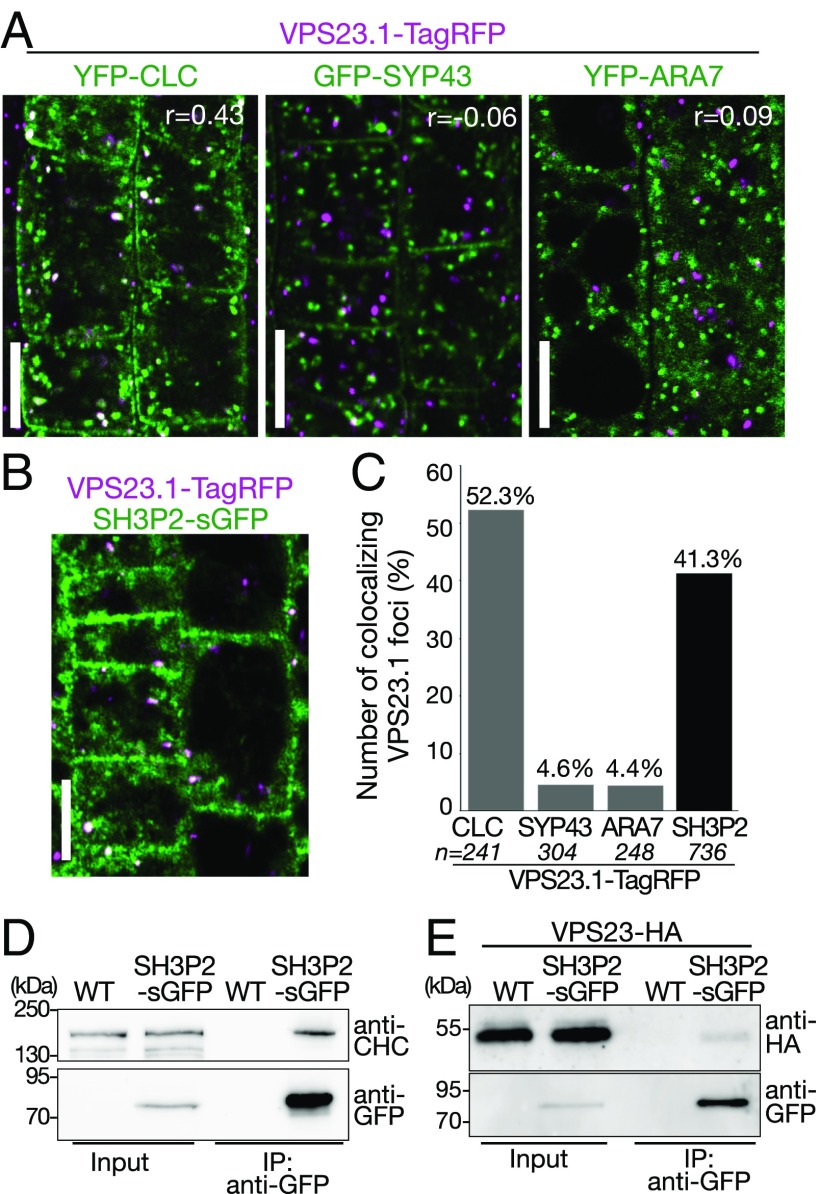
Fig. 3.
VPS23.1-TagRFP colocalizes with SH3P2-sGFP and YFP-CLC in planta. (A) Colocalization analysis of VPS23.1-TagRFP with endosomal markers. Colocalization of VPS23.1-TagRFP with the clathrin marker YFP-CLC (Left), the early endosome marker GFP-SYP43 (Center), and the late endosome marker YFP-ARA7 (Right) was analyzed with a confocal microscope in root epidermis cells of 7-d-old Arabidopsis seedlings. r, Pearson’s correlation coefficient. (Scale bars: 10 μm.) (B) Colocalization of VPS23.1-TagRFP and SH3P2-sGFP. The localization of VPS23.1-TagRFP and SH3P2-sGFP in root epidermis cells of 7-d-old seedlings was analyzed under a confocal microscope. (Scale bar: 10 μm.) (C) Percentage of VPS23.1-TagRFP–positive foci that colocalize with endosomal markers or SH3P2-sGFP shown in A and B. n, total numbers of analyzed VPS23.1-TagRFP foci. (D) CHC coimmunoprecipitates with SH3P2-sGFP. Total extracts of 7-d-old wild-type (WT) and SH3P2-sGFP–expressing seedlings were incubated with anti-GFP antibody-immobilized agarose. After intensive washing, bead-bound materials [immunoprecipitated (IP) material: anti-GFP] and total extracts (input) were subjected to immunoblotting using anti-CHC and anti-GFP antibodies. (E) VPS23.1-HA coimmunoprecipitates with SH3P2-sGFP. Total extracts of WT and SH3P2-sGFP seedlings expressing VPS23.1-HA were incubated with anti-GFP antibody-immobilized agarose. After intensive washing, the IP material (anti-GFP) was subjected to immunoblots together with the total extracts (input) using anti-HA and anti-GFP antibodies.