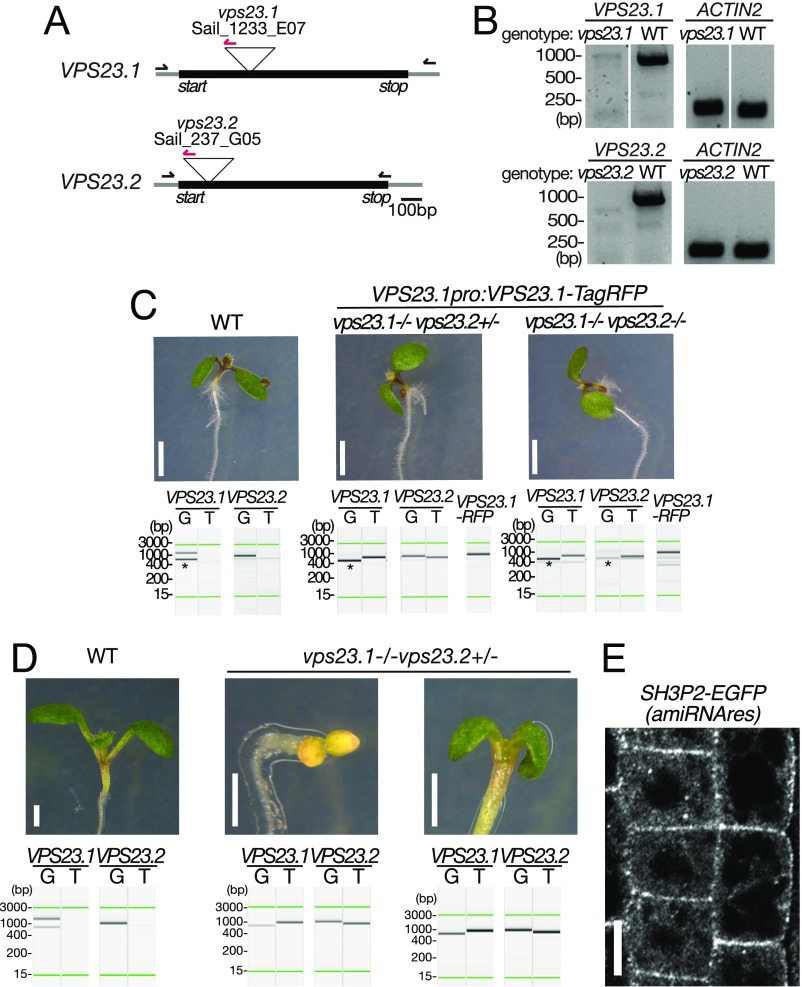
Fig. S7.
VPS23.1:VPS23.1-RFP complements seedling lethality of the vps23.1-3vps23.2-1 double-homozygous mutant. (A) Schematic presentation of the T-DNA insertion sites in vps23.1-3 and vps23.2-1. Gray lines indicate untranslated regions, and introns and black boxes indicate exons. The positions of start and stop codons are indicated in the figure. Binding sites of the forward and reverse primers and the T-DNA left border primer used for genotyping are indicated by arrows. (B) Expression of VPS23.1 and VPS23.2 in wild-type (WT), vps23.1-3, and vps23.2-1 seedlings was analyzed with VPS23.1-, VPS23.2-, and ACTIN2-specific primers. (C) Photographs of 7-d-old vps23.1-3vps23.2-1 seedlings. Photographs of WT (Left), vps23.1-3−/−vps23.2-1+/− (Center), and vps23.1-3−/−vps23.2-1−/− (Right) seedlings complemented with VPS23.1-TagRFP. PCR-based genotyping was conducted to verify the genotypes. Lanes G, genomic fragments; lanes T, T-DNA insertion-specific products. The green lines represent the 15-bp and 3,000-bp marker lines, respectively. The presence of the VPS23.1-TagRFP transgene was verified using construct-specific PCR primers. (Scale bars: 2 mm.) (D) Photographs of 7-d-old vps23.1-3−/−vps23.2-1+/− seedlings. Photographs of WT (Left) and vps23.1-3−/−vps23.2-1+/− (Center and Right) are shown. PCR-based genotyping was conducted to verify the genotypes, shown below the pictures. (Scale bars: 1 mm.) (E) Expression and localization of the amiRNA-resistant SH3P2:SH3P2(amiRNAres)-EGFP was observed under a confocal microscope. (Scale bar: 10 μm.)