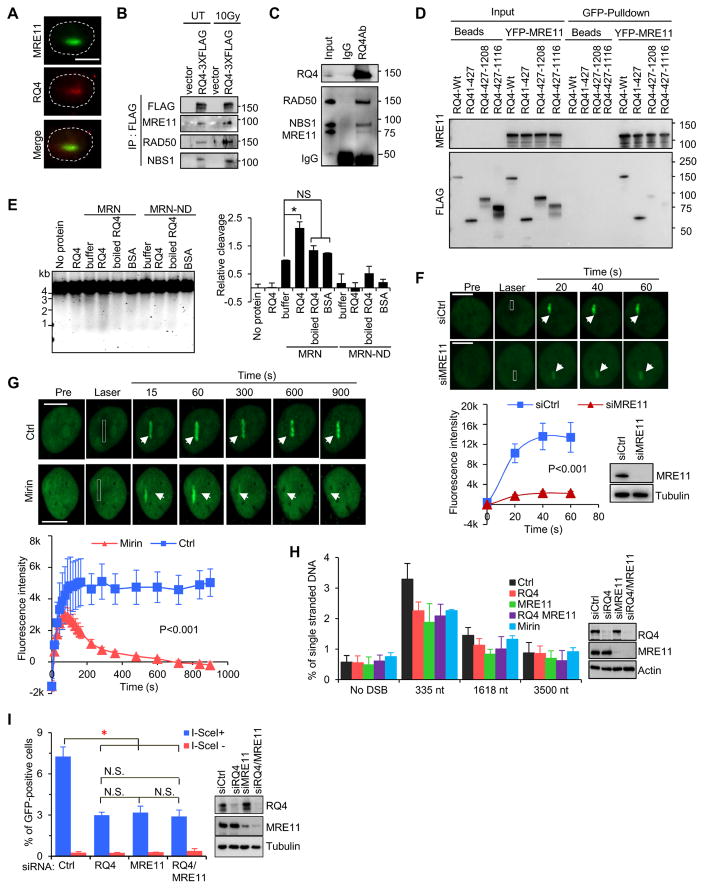
Figure 2.
MRE11 mediates recruitment of RECQL4 to DSBs to promote HR repair. A. Co-localization of endogenous RECQL4 and MRE11 at laser-induced DSB tracks in U2OS cells. Bar, 10 μm. B. RECQL4 interacts with MRN complex in vivo. FLAG-IP was carried out using extracts prepared from vector and RQ4-3xFLAG expressing HEK293T cells treated with a 10 Gy IR and recovered for 10 min. C. Co-IP of recombinant MRE11, RAD50 and NBS1 with RECQL4. D. N-terminal domain of RECQL4 interacts with MRE11. E. Nuclease of MRN is stimulated by RECQL4 on closed circular single strand PhiX174 DNA. MRN (20 nM) or the nuclease-dead mutant, MRN-ND, was incubated with 20 nM RECQL4, boiled RECQL4, or BSA. Buffer, nuclease reaction buffer. F. MRE11 promotes RECQL4 recruitment to DSBs in U2OS cells. The recruitment of GFP-RECQL4 to DSB tracks, generated with 435 nm laser, was monitored in the control and MRE11-depleted U2OS cells and the fluorescence intensity were quantified. n=27. Bar, 10 μm. G. Retention of RECQL4 at DSBs depends on the exonuclease activity of MRE11. U2OS cells were treated with100 μM mirin. Graphic quantification below images, n=21. Bar, 10 μm. H. RECQL4 and MRE11 regulate resection at DSBs. Bar graph showing percent of ssDNA content generated at DSB1 in siRNA- or mirin-treated cells. Error bars represent SEM from four biological repeats. I. HR repair assay and western blots from RECQL4 and MRE11 knockdown DR-GFP cells. All data are presented as mean ± SEM from at least three independent experiments with P-value calculated with Student’s t-test. *, P<0.05. See also Figures S3, Figure S4 and Table S1.