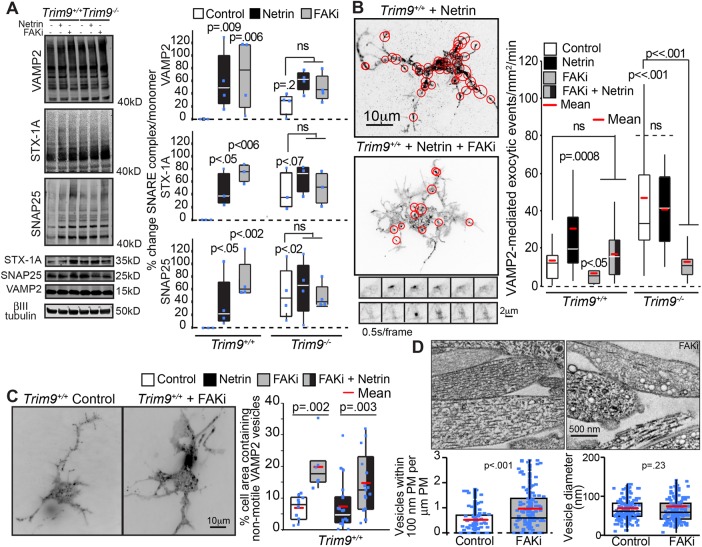
FIGURE 6:
Inhibition of FAK activity blocks SNARE-mediated exocytic vesicle fusion but not SNARE-complex formation. (A) Immunoblots and quantification of SNARE complexes (above 40 kDa) and monomers for VAMP2, syntaxin-1 (STX-1A), and SNAP25 shows that netrin-1 stimulation, genetic loss of Trim9, or FAKi treatment increases the accumulation of SNARE complexes in cortical neurons. The p values are from Kruskal-Wallis ANOVA with LSD post hoc correction compared with Trim9+/+ control, unless otherwise noted. (B) Quantification of VAMP2-pHluorin exocytic vesicle fusion events and example maximum projections of inverted time-lapse TIRF images of Trim9+/+ neurons expressing VAMP2-pHluorin treated with netrin-1 or netrin-1 and FAKi. Red circles indicate sites of vesicle fusion events. Montages represent examples of exocytic fusion events in a soma (top) and neurite (bottom). The p values are from Kruskal-Wallis ANOVA with Bonferroni post hoc correction to Trim9+/+ control, unless otherwise noted. (C) Average projection of TIRF time-lapse images of GFP-VAMP2 vesicles in Trim9+/+ control and FAKi-treated neurons. Quantification of percent of the total cell area containing nonmotile vesicles. The p values are from Kruskal-Wallis ANOVA with Tukey post hoc correction. (D) Representative transmission electron micrographs of Trim9+/+ control and FAKi-treated neurons reveals an increase in vesicle-like structures near the plasma membrane of FAKi-treated cells. Left, density of vesicles within 100 nm of the plasma membrane; p value from Mann-Whitney test. Right, vesicle diameter; p value from t test.