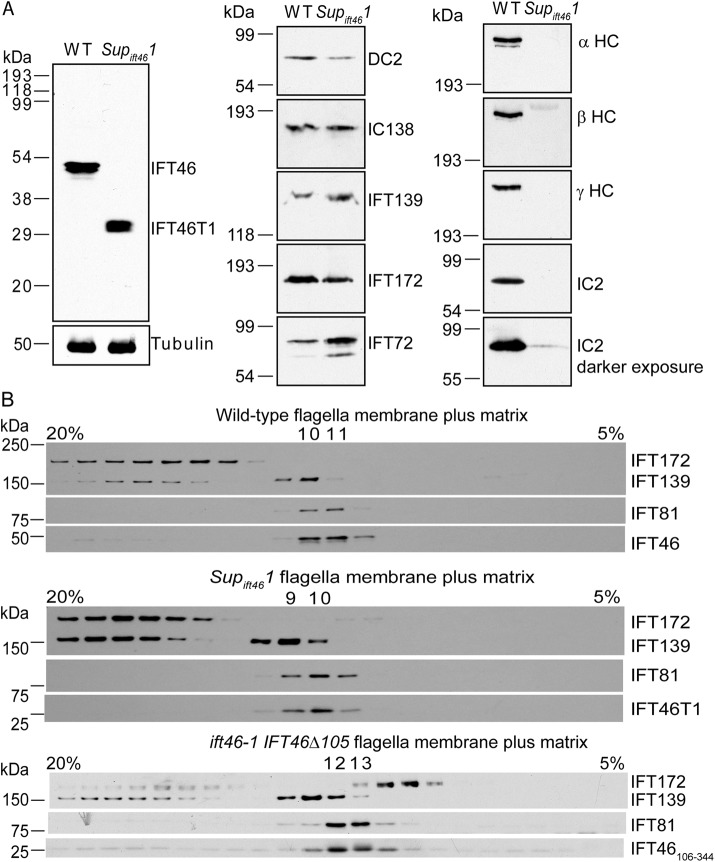
FIGURE 2:
IFT46T1 and IFT46106-344 incorporate into the IFT-B1 subcomplex in Supift461 and ift46-1 IFT46Δ105 flagella, respectively. (A) Western blots of isolated flagella of wild type and Supift461. Left, a blot probed with the anti-IFT46C antibody, which specifically recognizes IFT46 at ∼48 kDa in the wild-type sample (WT) and IFT46T1 at ∼30 kDa in the Supift461 sample. Tubulin served as a loading control. Center and right, blots of the same samples probed for the indicated proteins. Inner arm dynein intermediate chain IC138 is present at near-normal levels in Supift461 flagella but outer arm dynein α, β, and γ heavy chains and intermediate chain IC2 are missing or greatly reduced. DC2, an outer arm dynein docking-complex protein that is transported into flagella independently of outer arm dynein (Takada and Kamiya, 1994; Wakabayashi et al., 2001), is slightly reduced in Supift461 flagella; this is expected for flagella lacking the outer dynein arm (Wakabayashi et al., 2001). (B) IFT46T1 and IFT46106-344 comigrate with the IFT-B1 subcomplex. Flagellar membrane-plus-matrix fractions from wild-type (top), Supift461 (middle), or ift46-1 IFT46Δ105 (bottom) cells were further fractionated on 5–20% sucrose gradients, and the fractions were analyzed by Western blotting using antibodies to the indicated IFT proteins. IFT-B1 proteins migrated together as shown by IFT81 and IFT46 in the wild-type sample. Like their wild-type counterpart, both IFT46T1 and IFT46106-344 comigrated with the IFT-B1 protein IFT81.