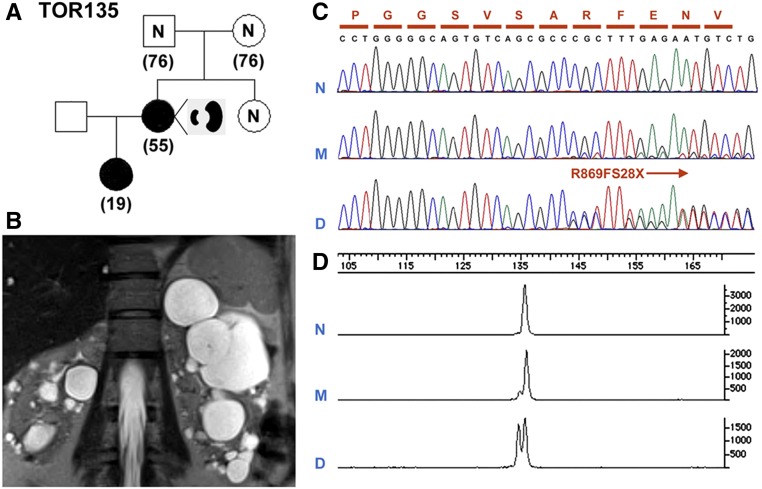
Figure 6.
An example of PKD1 somatic mosaicism. (A) A pedigree (TOR135) with somatic mosaicism and germline disease transmission. (B) MRI shows asymmetric PKD in the affected mother with somatic mosaicism. (C) Sanger sequencing showing a 1-bp PKD1 frameshift deletion (c.2605delC; p.R869FS28X) unequivocally in the daughter (D) but not in the mother (M). (D) Quantitative analysis by capillary electrophoresis of the PCR product encompassing the PKD1 mutation site shows that the ratio of mutant to normal alleles is approximately 1:1 in the daughter (D) but only approximately 1:10 the mother (M).