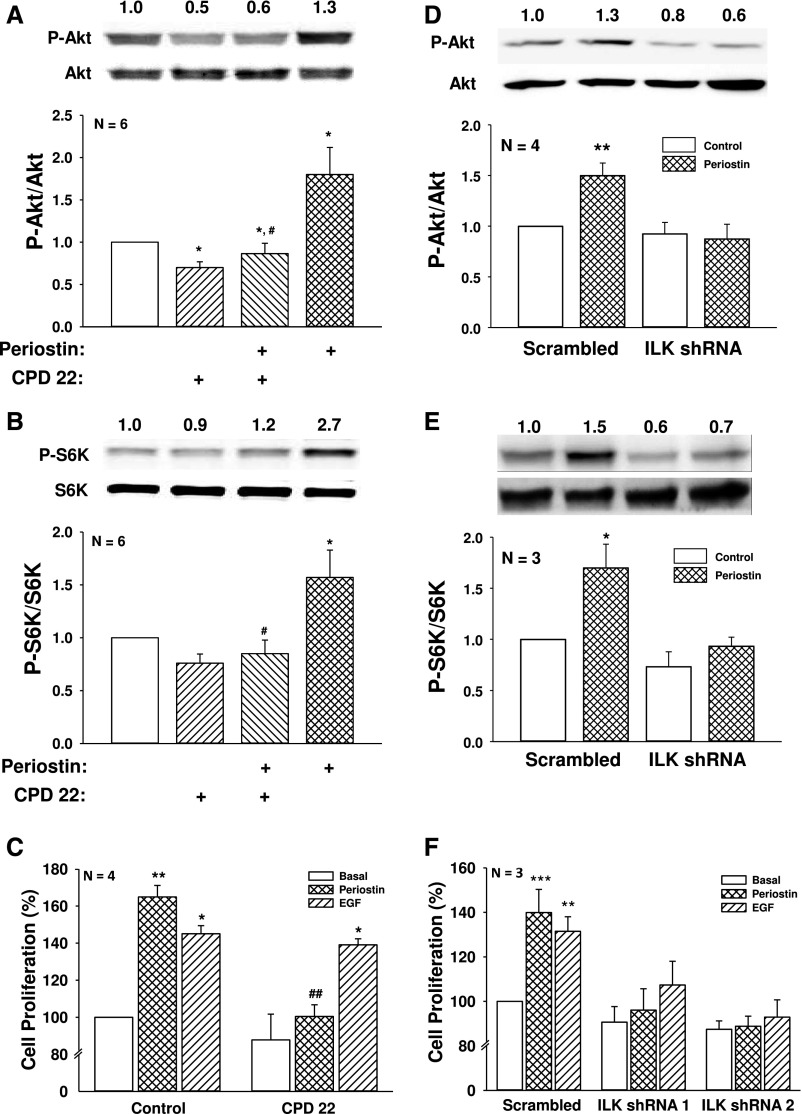
Figure 2.
ILK inhibition or knockdown prevents periostin-induced Akt/mTOR signaling and ADPKD cell proliferation. ADPKD cells were treated with or without 2.5 µM CPD 22 for 1 hour and then periostin was added for an additional 15 minutes. Immunoblot analysis was used to measure (A) P-Akt/Akt and (B) P-S6K/S6K. (C) The effect of ILK inhibition on ADPKD cell proliferation was determined by treating cells with 250 ng/ml periostin or 25 ng/ml EGF for 48 hours in the presence or absence of 1 µM CPD 22. Cell numbers were counted using a BioRad TC20 cell counter. To confirm the role of ILK, ADPKD cells were infected with lentivirus containing shRNA against ILK or a nonspecific (scrambled) sequence. Cells were treated with 250 ng/ml periostin for 15 minutes and levels of (D) P-Akt and (E) P-S6K were measured by immunoblot analysis. Summary data for (D) P-Akt/Akt and (E) P-S6K/S6K were normalized to basal conditions of scrambled shRNA cells (set to 1.0). (F) ADPKD cells were infected with an ILK (shRNA 1 or shRNA 2) or a scrambled shRNA lentivirus, and then treated with periostin or 100 ng/ml EGF for 24 hours. Cell proliferation was measured by Promega MTT assay and normalized to basal proliferation of cells infected with the scrambled shRNA (set to 100%). Cell proliferation was also confirmed by counting cell numbers (Supplemental Figure 2, B and C). *P<0.05, **P<0.01, and ***P<0.001, compared with control or basal conditions of scrambled shRNA infected cells, and #P<0.05, ##P<0.01, compared with periostin alone.