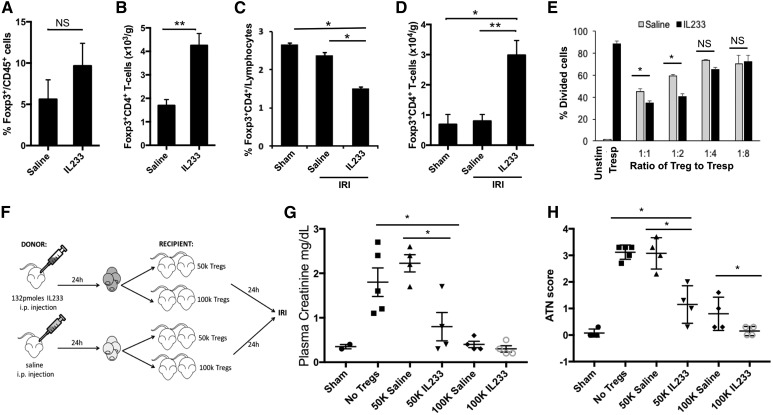
Figure 4.
IL233 fusion cytokine enhances mobilization, intrarenal levels, suppressive function, and the protective ability of Tregs. B6 mice were injected intraperitoneally for five consecutive days with 66 pmol per mouse per day of IL233 (n=7) or saline (n=5). (A) Proportion of CD4+Foxp3+ Tregs in the CD45 gate and (B) absolute number of Tregs were analyzed in the kidney by flow cytometry. Mice treated with 66 pmol per mouse per day of IL233 (n=10) or saline (n=8) for 5 days were subjected to 26 minutes of bilateral ischemia on day 8 and analyzed 24 hours later for Tregs in spleen (C) and kidneys (D). (E) Tregs were isolated from mice treated with saline or IL233 (single injection of 132 pmol 24 hours before isolation of cells) and compared for their ability to suppress proliferation of naïve CD4+ T cells (responder T cells [Tresp]) in a CFSE dilution assay. IL233 treatment improved the in vitro suppressive ability of Tregs. Mean±SEM is shown in bar graphs (A–E). (F) Mice were injected either with saline or a single dose of 132 pmol of IL233, and 24 hours later, Tregs were isolated from the spleens of these mice. The isolated Tregs (50×103 or 100×103 per mouse, administered intravenously; or saline as control) were then injected into recipient mice; 24 hours later, the recipient mice were subjected to 26 minutes of bilateral ischemia. PCr (G) and ATN score (H) were analyzed after 24 hours of reperfusion. Tregs isolated from IL233-treated mice offered better protection to the recipients than Tregs isolated from saline-treated mice. Symbols represent individual mice; mean±SEM is shown. *P<0.05; **P<0.01.