Figure 1.
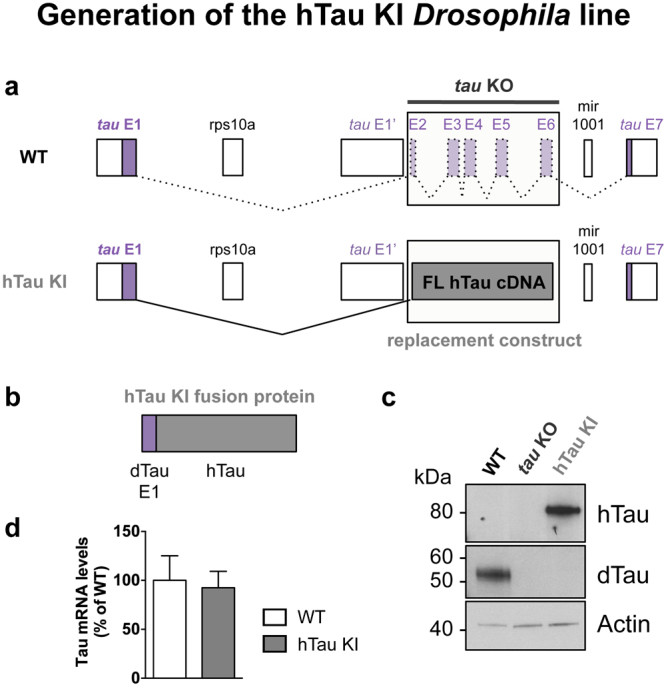
Generation of the hTau KI Drosophila line. (a) Schematic representation of the genetic region encompassing the tau gene in Drosophila. Coding exons of Drosophila tau are represented in purple. hTau full-length (2N4R) cDNA sequence (grey) was inserted in place of tau exons 2–6 to generate the hTau KI fly line. A more detailed representation is shown in Supplementary Figure 1. (b) The expected hTau KI protein product is a fusion of dTau exon 1 (purple) and hTau (grey) (c). Western blot analysis of head extracts from WT, tau KO and hTau KI flies using anti-hTau and anti-dTau antibodies, indicated that hTau was expressed following its knock-in into the endogenous fly tau locus. The apparent molecular weight of the hTau KI protein was 80 kDa. No dTau proteins were expressed in homozygous hTau KI flies. Actin is shown as a loading control (western blots were cropped in this figure; full blots are shown in Supplementary Figure 15). (d) Tau mRNA levels measured by qRT-PCR in heads of 20-day-old hTau KI flies were comparable to those of WT flies (p > 0.05, Student’s t-test, n = 3–5 biological replicates). Primers were designed to detect fly tau exon 1, present in both fly lines.
