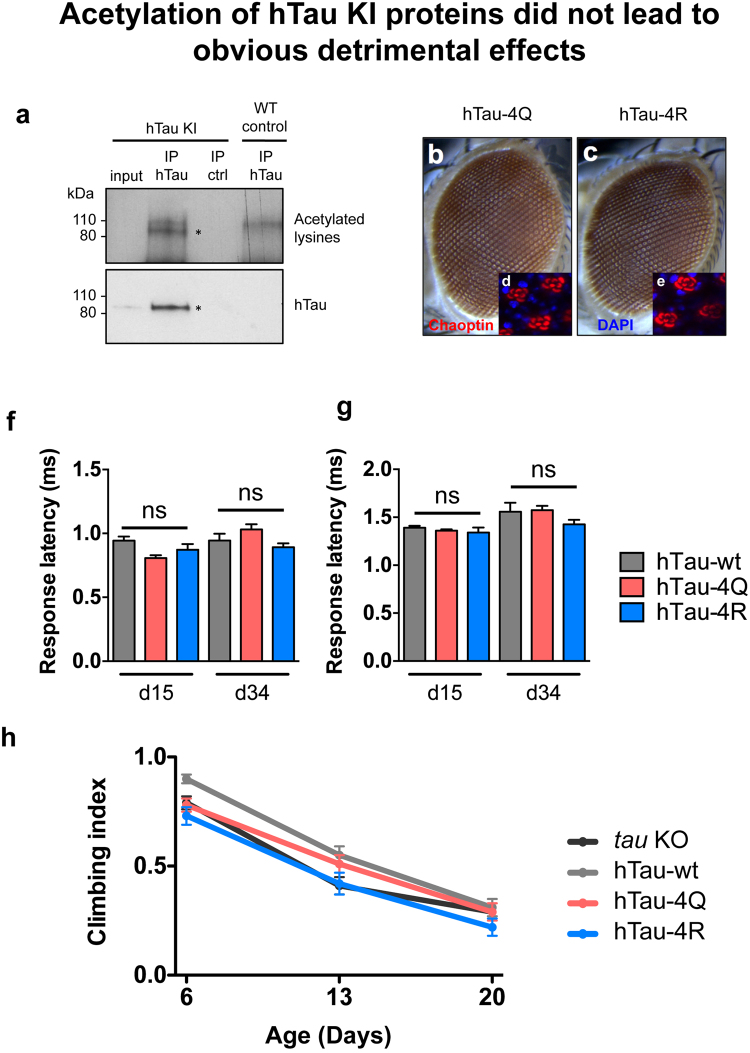
Figure 5.
Acetylation of hTau KI proteins did not lead to obvious detrimental effects. (a) hTau proteins were acetylated in hTau KI Drosophila. Immunoprecipitation of hTau followed by western blot against acetylated lysines (upper panel) and total hTau proteins (lower panel) revealed a specific band for acetylated hTau species (asterisk), indicating that hTau proteins were acetylated in hTau KI fly heads. hTau immunoprecipitation on protein extracts from WT flies was performed as a negative control. Western blots were cropped in this figure; full blots are shown in Supplementary Figure 17. (b and c) Representative eye pictures of 3-day-old hTau-4Q (b) and hTau-4R (c) flies. Scale bar: 100 μm. (d and e) Photoreceptor loss in fly retinas was evaluated by anti-Chaoptin immunofluorescence (red) in 3-day-old hTau-4Q (d) and hTau-4R (e) KI flies. DAPI was used to stain cell nuclei (blue). Scale bar: 5 μm. (f and g) Electrophysiology recordings in the TTM (f) and DLM (g) was performed in 15- and 34-day-old hTau-wt, hTau-4Q and hTau-4R KI flies and showed no significant difference in neurotransmission through the giant fiber neuronal system among the investigated lines (p > 0.05, one-way ANOVA). (h) Climbing analysis was performed on hTau-wt, hTau-4Q, hTau-4R and tau KO control flies throughout ageing, showing no detrimental effect of hTau expression on fly climbing.