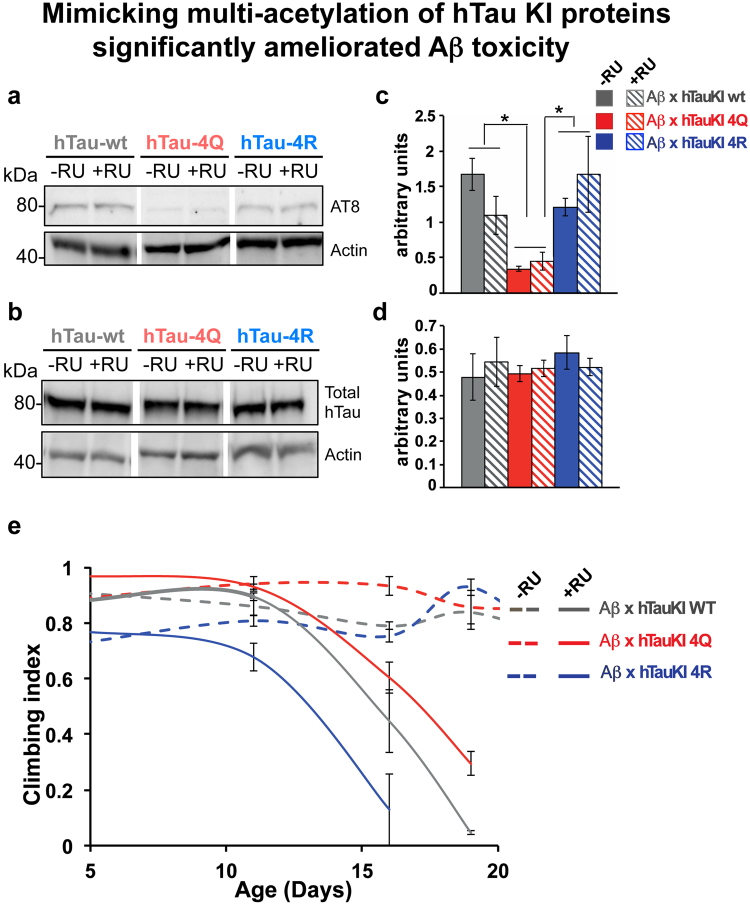
Figure 8.
Mimicking multi-acetylation of hTau KI proteins ameliorated Aβ toxicity. (a) Western blot analyses (a and b) and quantification (c and d) of hTau phosphorylation (AT8) and total hTau levels were carried out respectively on head extracts of 12 day-old flies either co-expressing Aβ (+RU) with the different homozygous hTau KI lines, hTau-wt, hTau-4Q and hTau-4R, or expressing homozygous hTau KI lines alone (−RU), grown at 28 °C. Results were normalised to Actin. (n = 3/genotype, *p < 0.05, one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s post hoc test). Western blots were cropped in this figure. Full blots are shown in Supplementary Figure 20. (e) Climbing assay shows that the flies co-expressing Aβ (+RU) and homozygous hTau-4Q line have improved climbing (n = 3, *p < 0.05, beta regression analyses) and flies co-expressing Aβ (+RU) and homozygous hTau-4R line climb worse (n = 3, ****p < 0.0001, beta regression analyses) in comparison to control flies co-expressing Aβ (+RU) and homozygous hTau-wt. Homozygous hTau KI lines (−RU) alone did not differ in their climbing ability. Genotype of flies expressing Aβ42 arc in the different hTauKI homozygous backgrounds, Aβ42 arc/+; hTauKI (wt, 4R or 4Q)/elavGS,hTauKI (wt, 4R or 4Q).