Fig. 1.
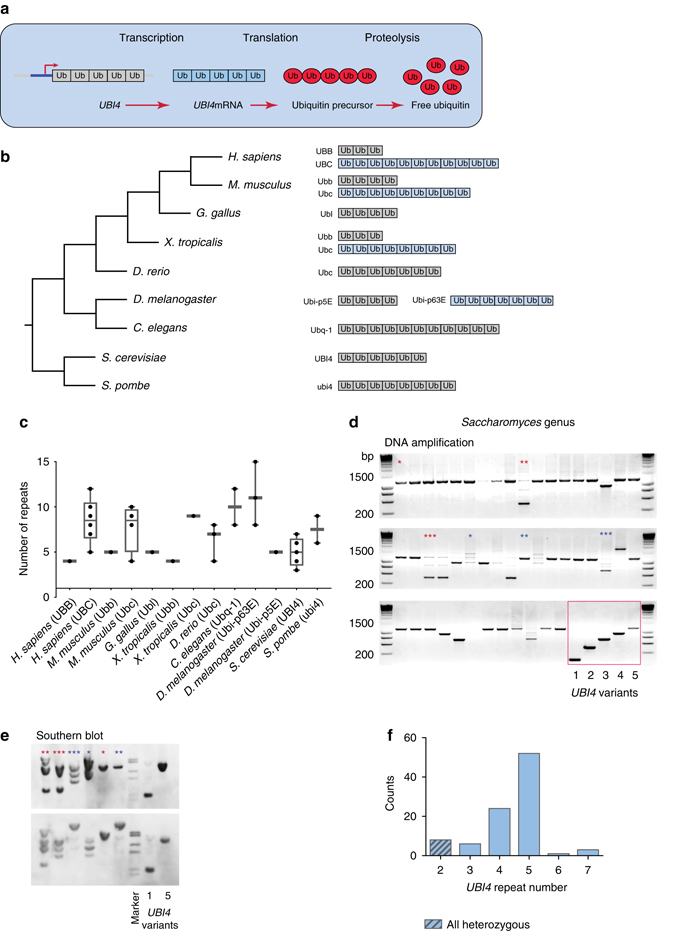
The number of ubiquitin moieties encoded by the eukaryotic polyubiquitin gene is evolutionary unstable and varies among species and strains. a The eukaryotic polyubiquitin gene (e.g., UBI4) is transcribed as a single transcript and translated into a multiunit ubiquitin precursor that is subsequently cleaved into free ubiquitin moieties by specific deubiquitinating enzymes. b Phylogenetic tree of various eukaryotic model organisms (left) and their polyubiquitin gene structure(s) (right). The variant containing the highest number of ubiquitin repeats is drawn (except for D. melanogaster). The gene names for each homologue in the Uniprot database are given. The polyubiquitin gene underwent a duplication event in several eukaryotic lineages (extra gene copy represented in blue). In the D. melanogaster lineage, the duplicated copies are in tandem. c Boxplot depicting the variation in polyubiquitin repeat number for various eukaryotic model organisms (see also b and Supplementary Data 1). d The polyubiquitin UBI4 gene was amplified from 98 strains belonging to the Saccharomyces genus in their natural ploidy. Shown are 48 representative strains. The framed section shows the amplification products of the different UBI4 gene variants constructed for this study in the Saccharomyces cerevisiae S288c lab strain, with the number under the lanes indicating the number of UBI4 repeats. Asterisks denote the products of DNA amplification and Southern blot (e) of the UBI4 gene originating from the same strains. e Southern blot analysis confirms the number of UBI4 repeats in a subset of the natural strains (d), and rules out that the differences in UBI4 length or the multiple bands shown in c are due to slippage during PCR amplification. Asterisks denote the products of DNA amplification and Southern blot of the UBI4 gene originating from the same strains. f Distribution of UBI4 repeat number in the Saccharomyces genus. The UBI4 allele of 2 units is always heterozygous with the other allele being ≥ 4 repeats
