Figure 3.
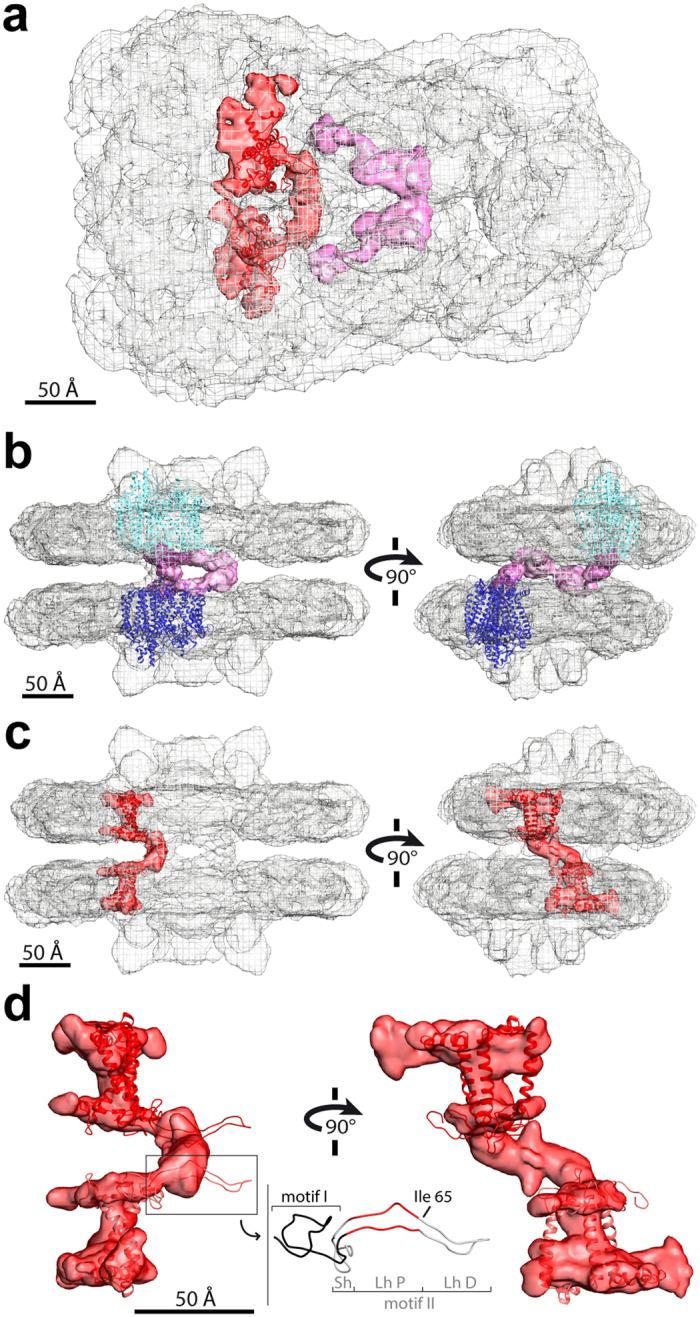
“Hinge” and “knot” connections cross the stromal gap of paired C2S2M supercomplexes. (a) Top view towards the luminal surface, showing the cryo-EM density map of paired C2S2M supercomplexes (grey mesh), with the stromal “hinge” density in magenta and the stromal “knot” density plus adjoining supercomplex region in red. Fitting of the high-resolution structure of Lhcb4 from spinach26 (PDB 3JCU: chain r; upper Lhcb4 in lighter red, lower Lhcb4 in darker red) as in Fig. 2 is shown. (b) Side and end views within the membrane plane showing the connections between the paired supercomplexes and the “hinge” (connecting supercomplex density in violet mesh). The hinge connects one PSII monomer of the upper supercomplex to one PSII monomer of the lower supercomplex (PDB 3JCU: chains A, C and D, corresponding to the subunits D1, CP43 and D2; upper PSII core in cyan, lower PSII core in blue)26. (c) Side and end views within the membrane plane showing the connections between the paired supercomplexes and the “knot”, which links an Lhcb4 of the upper supercomplex with an Lhcb4 of the lower supercomplex. Fitting of the high-resolution structure of Lhcb4 from spinach26 as in panel (a). (d) Enlarged views of the “knot” density plus adjoining supercomplex region fit with two Lhcb4 subunits, as in panel (c). The inset shows the N-terminal loop of the Lhcb4 structure by Wei et al.26, composed of motif I (Pro12–Lys41) in black and motif II (Pro42–Phe87) in grey and red. Motif II is subdivided into the short hairpin (Sh, Ala73–Phe87, grey), the proximal part of the long hairpin that fits within the “knot” cryo-EM density (Lh P, Pro42–Gln47 and Ile66–Ser72, red) and the distal part of the long hairpin that protrudes from the “knot” density (Lh D, Thr48–Ile65, grey). The flexible Ile65 residue, which separates the proximal and distal segments of the long hairpin, is indicated.
