Figure 1.
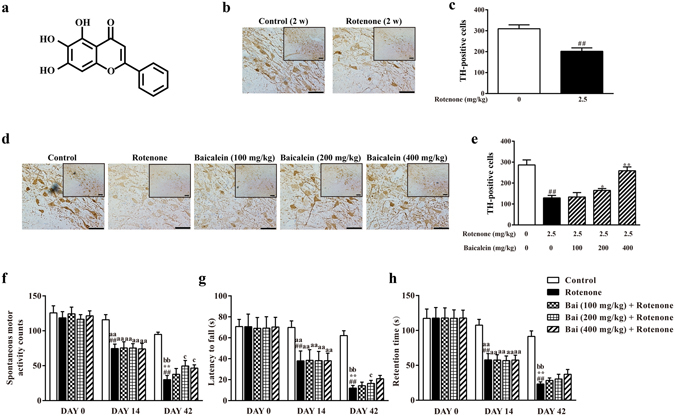
Effects of baicalein on the behavioural deficits and TH+ cell numbers in the SN in rotenone-induced PD rats. (a) Chemical structure of baicalein. The control solvent and rotenone were injected i.p. for 14 days to assess the effect of rotenone on TH+ cells in the SN. (b) Representative microphotographs of TH immunostaining and (c) quantification of the effect of rotenone on TH+ cells in the SN (scale bar: 50 μm). Values are expressed as the means ± SEMs. N = 15. Statistical analyses were performed using an unpaired sample t test. ##P < 0.01 compared with the control group. The effect of baicalein on the TH+ cell number was evaluated after administration of baicalein for 28 days along with rotenone injection for 42 days. (d) Representative microphotographs of TH immunostaining and (e) quantification of the effect of baicalein on TH+ cells in the SN (scale bar: 50 μm). Values are expressed as the means ± SEMs. N = 5. Statistical analyses were performed using one-way ANOVA. ##P < 0.01 compared with the control group, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 compared with the model group. Motor functions were assessed through a spontaneous motor activity test (f), rotarod test (g) and inclined plane test (h). DAY 0 and DAY 14 in the control and rotenone group: N = 15; Others: N = 10. Statistical analyses were performed using one-way ANOVA. ##P < 0.01 compared with DAY 0 in the rotenone group, **P < 0.01 compared with DAY 14 in the rotenone group, aaP < 0.01 compared with DAY 14 in the control group, bbP < 0.01 compared with DAY 42 in the control group, cP < 0.05 compared with DAY 42 in the rotenone group.
