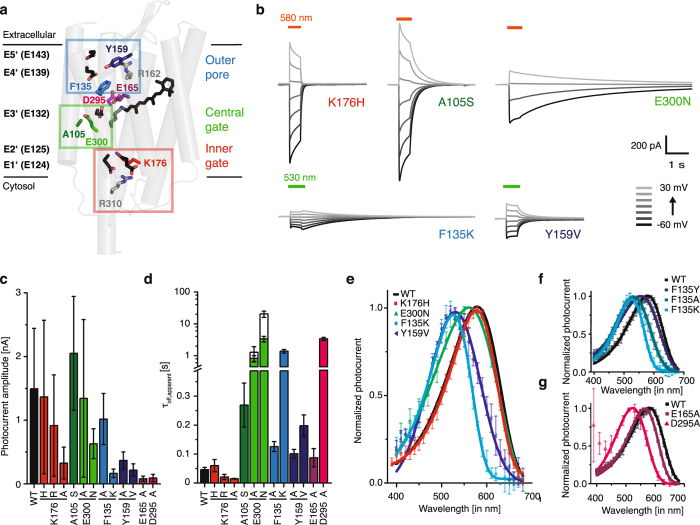
Figure 4.
Mutation analysis of substitutions along the ion conducting pathway. (a) Homology model of Chrimson (based on C1C2 4yzi.pdb) with pore lining glutamates E1’ to E5’ (in black) and amino acid substitutions compared to C1C2 in the inner gate (red), central gate (green) and the outer pore (blue) (b) Representative photocurrents of Chrimson mutants (incorporating one-by-one the corresponding residues of C1C2) at different voltages in symmetric 110 mM NaCl and pHi,e 7.2 (c) Photocurrent amplitudes of WT and pore mutants at −60 mV and symmetric 110 mM NaCl and pHe,i 7.2 (mean ± SD; WT n = 16 cells; K176H n = 10, K176R n = 14, K176A n = 8, A105S n = 16, E300A n = 8, E300N n = 10, F135A = 18, F135K = 18, Y159A n = 6, Y159V n = 7, E165A n = 7, D295A n = 5). (d) Apparent off-kinetics at −60 mV τapparent,off,−60mV of Chrimson WT and pore mutants at pHe,i 7.2. Empty columns for E300A and E300N represent conductance measurements by short 20 ms voltage pulses to −60 mV at 0.5 Hz and a holding potential of 0 mV for the reduction of current decline due to intracellular acidification (mean ± SD; WT n = 18 cells; K176H n = 9, K176R n = 7, K176A n = 8, A105S n = 13, E300A n = 8/2, E300N n = 10/8, F135A = 18, F135K = 17, Y159A n = 6, Y159V n = 7, E165A n = 7, D295A n = 5) (e) Normalized peak photocurrents after 10 ms excitation at different wavelengths of equal photon count for selected mutants (mean ± SD; symmetric 110 mM NaCl, pHe,i 7.2 and −60 mV; WT n = 10 cells; K176H n = 7, E300N n = 8, F135K = 11, Y159V n = 7), (f) different mutants of F135 (mean ± SD; WT n = 10, F135K n = 11, F135Y n = 7, F135A n = 15) (g) and of putative counter ion mutants (mean ± SD; WT n = 10, E165 n = 11, D295 n = 7).