Figure 6. Proposed signalling pathway for the modulation of TASK‐1 channels in dLGN IN.
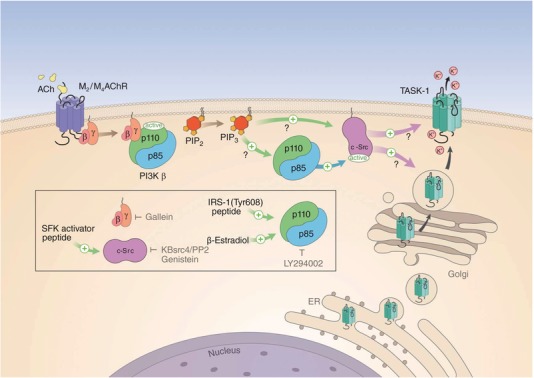
Binding of ACh to Gi/o‐protein‐coupled M2/M4AChR (the α subunit is not shown) leads to the activation of PI3Kβ via binding of the G‐protein βγ subunit. While the inhibition of the catalytic p110 subunit by the regulatory p85 subunit is released, the SH2 domain‐dependent interaction of p85 with c‐Src leads to activation of TK activity. c‐Src activation increases current through TASK‐1 (or TASK‐1,3) channels by direct interaction (as indicated by the short time scale of minutes of the Oxo effect) with the channel protein. Facilitation of trafficking and integration of channels into the membrane (possible via the adapter proteins p11 and 14‐3‐3) is a potential second mechanism. The product of p110 enzymatic activity, the phospholipid PIP3, potentially facilitates the interaction between the components of the receptor cascade, which may be arranged in close spatial proximity. The box indicates the sites of action of enzyme activators (green arrows) and inhibitors (depicted by grey ┬ symbols) used in the present study.
