Figure 11. Previous physical training protects against FPI‐induced spatial learning dysfunction.
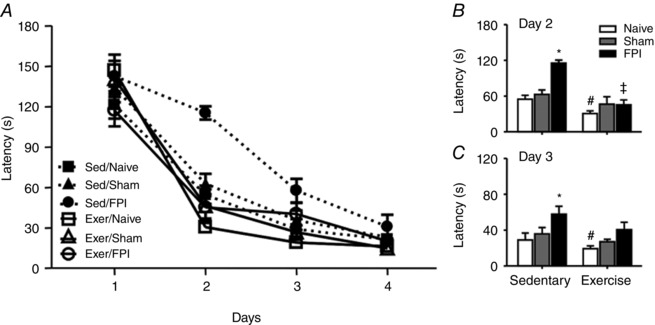
Exercise training and FPI effects on escape latency in Barnes maze test (A). B and C, previous swimming training decreased the latency for escape per se and protected against latency for escape increase induced by FPI. Data are the mean ± SEM (n = 7–9 in each group). * P < 0.05 compared to sham and naive sedentary group. # P < 0.05 compared to the naïve‐sedentary group.
