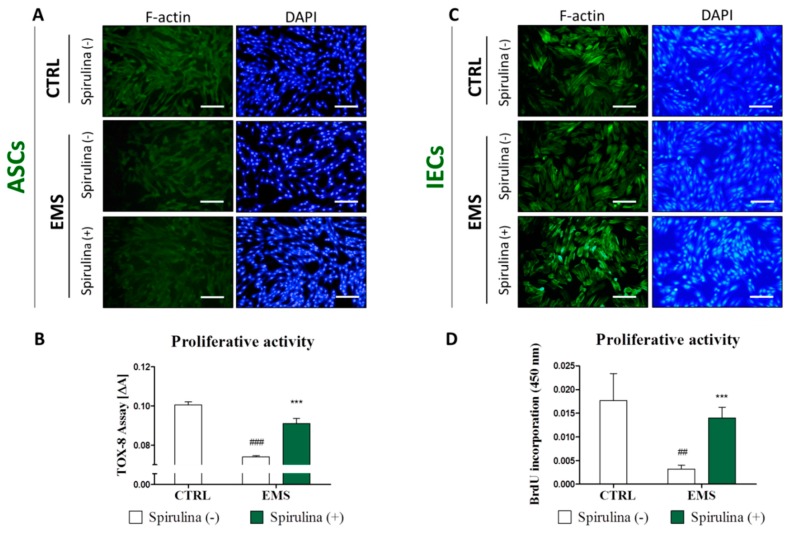
Figure 2.
The effect of Spirulina treatment on equine adipose-derived mesenchymal stromal cells’ (ASCs’) and intestinal epithelial cells’ (IECs’) morphology and proliferative potential. Using fluorescence cell imaging technique allowed us to monitor the changes in the morphology of ASCs (A) and IECs (C) following exposition to Spirulina platensis aqueous extract. Actin filaments were visualized with atto-488-labeled phalloidin, the nuclei were counterstained with DAPI. Photographs presented in the graph are representative and show characteristic features of examined cultures. Cellular morphology of ASCEMS and IECEMS was slightly altered in reference to the corresponding control cells, however, this effect was attenuated by treating cells with Spirulina. Proliferative potential of ASCs (B) was evaluated after 24 h of treatment by measuring the metabolic activity of cells manifested by bioreduction of resazurin dye. IECs proliferation (D) was measured by colorimetric quantification of DNA synthesized in the presence of BrdU label. A significant upregulation of proliferation was observed in both investigated cell populations cultured in the presence of Spirulina platensis. Magnification 100×, scale bars: 250 μm. Results expressed as mean ± SD, ## p < 0.01, ###/*** p < 0.001.