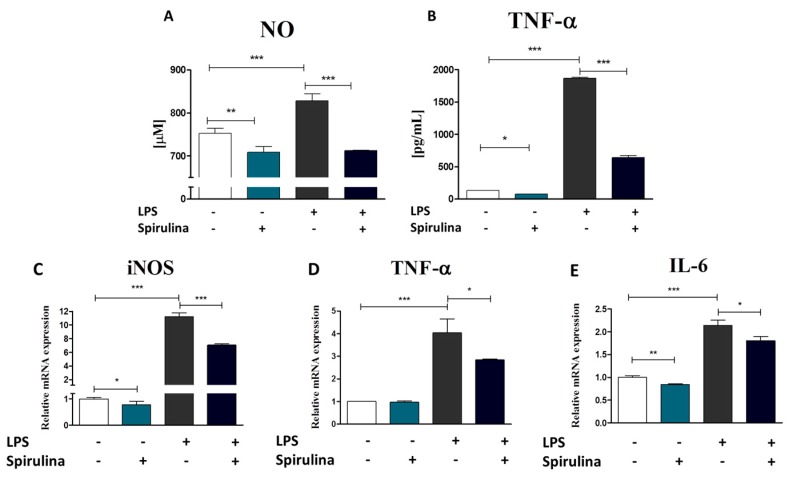
Figure 8.
The effect of Spirulina platensis on the activation status of murine peritoneal macrophages. Mouse macrophages were isolated from the total pool of peritoneal exudate cells and cultured in the presence or absence of Spirulina water extract for 24 h. Macrophage inflammatory responses were subsequently triggered by LPS (1 µg/mL). Supernatants were collected and assayed for NO (A) and TNF-α (B). Moreover, the effect of Spirulina pre-treatment on iNOS (c), TNF-α (D) and IL-6 (E) gene expression was evaluated by the means of real time RT-PCR. The data show that Spirulina treatment effectively inhibited LPS-induced production of secretory NO and TNF-α, as well as overexpression of iNOS, TNF-α, and IL-6 in peritoneal macrophages. Results are expressed as mean ± SD, * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001.