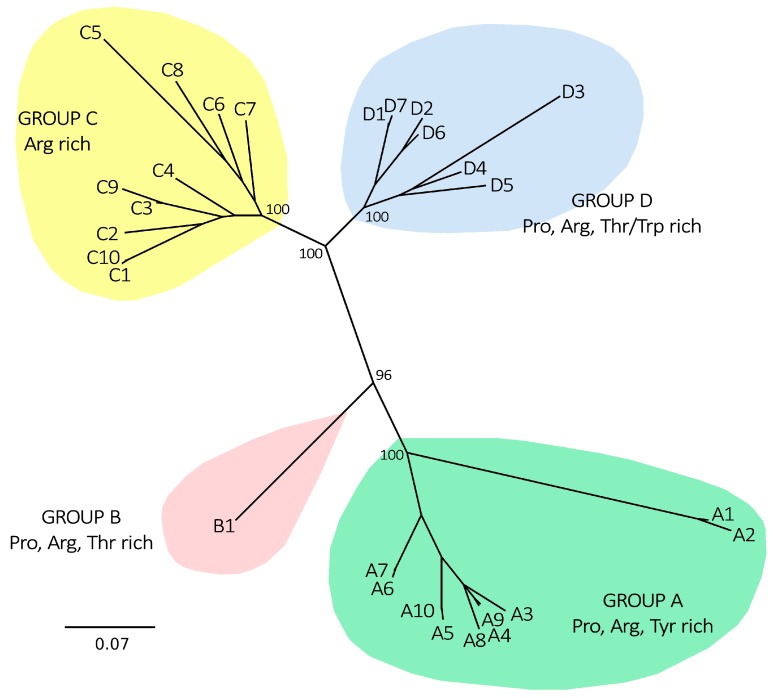
Figure 2.
Unrooted Bayesian phylogenetic tree summarizing the relationships among myticalins. The tree topology is based on the multiple sequence alignment of the nucleotide sequences encoding the precursor proteins of myticalins, with the hypervariable mature peptide region removed. Codon triplets were preserved and the tree topology was calculated based on a codon w variation model of molecular evolution. Only posterior probability support values for the major nodes are displayed for clarity’s sake. All the sequences displayed in the tree pertain to the Mytilus edulis species complex (M. galloprovincialis, M. edulis, M. trossolus and M. chilensis), with the exception of myticalin A1, A2, A6, A7, C4 and C7, which were detected in M. californianus.