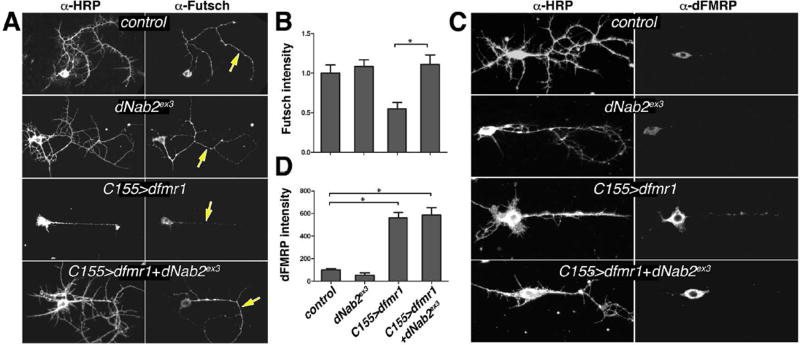
Figure 5. dNab2 plays a more minor role in futsch regulation.
Paired images of (A) anti-Futsch or (C) anti-dFMRP labelled 24h APF brain neurons co-stained with anti-HRP. Genotypes: control (elavC155), dNab2ex3 (elavC155;dNab2ex3/ex3), C155>dfmr1 (elavC155>UAS-dfmr1), or C155>dfmr1+dNab2ex3 (elavC155>UAS-dfmr1;dNab2ex3/ex3). Yellow arrows highlight differences in Futsch staining in central processes. Quantitation of (B) Futsch (n=15 shafts) or (D) dFMRP (n=12 shafts) levels presented as mean fluorescence intensity from individual neuronal processes among the same genotypes as in A and C. Data are normalized to control (elavC155) in each graph. Error bars=SEM (*p<0.05).