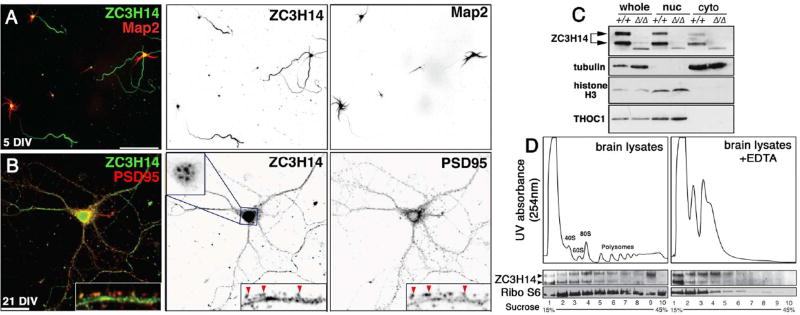
Figure 7. ZC3H14 localizes to axons in primary hippocampal neurons and associates with polyribosomes in mouse cortical lysates.
(A,B) Confocal images of primary hippocampal neurons cultured 5 or 21 days in vitro (DIV) from P1 (post-natal day 1) mice and stained with anti-ZC3H14 (green) and (A) anti-Map2 (red) or (B) anti-PSD95 (red). Scale bars=50 µm. Individual channels are presented as inverted grayscale images. Magnified insets in B show distribution of ZC3H14 in dendritic shafts and PSD95-positive spines (red arrowheads). ZC3H14 in 21 DIV neurons is shown at reduced gain in order to resolve nuclear speckles in this cell type (Pak et al., 2011). (C) Immunoblot of fractionated Zc3h14+/+ and Zc3h14Δ13/Δ13 brains to detect ZC3H14, α-Tubulin (cytoplasmic marker), Histone H3 (nuclear marker), and THOC1, a nuclear RBP. (D) Cytoplasmic polysome profiles of wt P13 brain cortexes across a 15–45% linear sucrose gradient prepared +/− EDTA with 254nm absorption profiles (ribosomes and polysomes are indicated). Lower panels show immunoblot for ZC3H14 and S6 ribosomal protein (Ribo S6) across the indicated fractions.