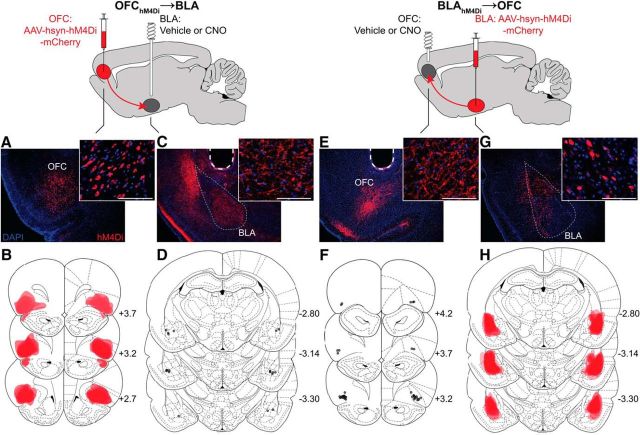
Figure 2.
Viral expression and cannulae placements. A–D, OFChM4Di→BLA rats (n = 10). Bilateral hsyn-hM4Di-mCherry injections were made into the OFC, and guide cannulae were implanted above the BLA, such that CNO infusion would inactivate OFC terminals in the BLA. A, Representative fluorescent image of hM4Di-mCherry expression in the OFC. Scale bars, 100 μm. B, Schematic representation of hM4Di-mCherry maximal viral spread in the OFC for all subjects. Numbers to the bottom right of each section indicate distance anterior to bregma (mm). Coronal section drawings taken from Paxinos and Watson (1998), their Figures 6–9 and 31–33, reprinted with permission. C, Representative immunofluorescent image of hM4Di-mCherry expression in the BLA. Dashed line indicates guide cannula track. D, Schematic representation of microinfusion injector tips in the BLA. E–H, BLAhM4Di→OFC rats (n = 19). Bilateral hsyn-hM4Di-mCherry injections were made into the BLA, and guide cannulae were implanted above the OFC, such that CNO infusion would inactivate BLA terminals in the OFC. E, Representative immunofluorescent image of hM4Di-mCherry expression in the OFC. F, Schematic representation of microinfusion injector tips in the OFC. G, Representative fluorescent image of hM4Di-mCherry expression in the BLA. H, Schematic representation of hM4Di-mCherry maximal viral spread in the BLA for all subjects.