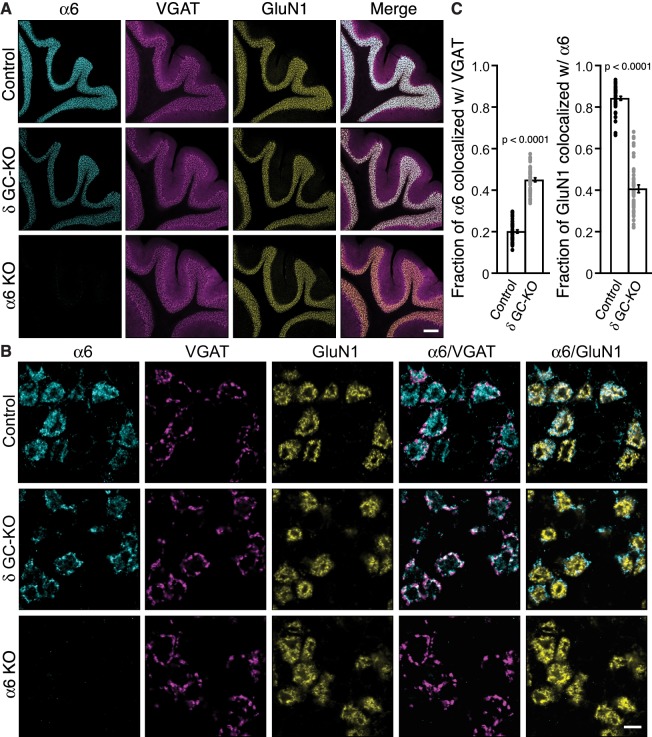
Figure 5. Delta inhibits synaptic localization of α6-containing GABAARs.
(A–C) The distribution of α6 was examined in the cerebellum of δ GC-knockout (KO) and α6 KO mice. Inhibitory presynaptic VGAT and excitatory postsynaptic GluN1 were co-stained. (A) Low magnification images showed specific α6 signal in cerebellar granular layers in wild-type (Control) and δ KO mice, but not in α6 KO mice. The images are representative from three animals for each genotype. (B) High-magnification representative images showed VGAT around the glomeruli and GluN1 inside the glomeruli. In control mice, α6 signal was diffuse over the glomeruli, and overlapped substantially with GluN1. In contrast, in δ KO mice, α6 signal was largely confined to the peripheral glomeruli where it colocalized with VGAT. (C) The fraction of α6 signal co-localized with VGAT was increased in δ KO mice, whereas the fraction of GluN1 signal co-localized with α6 signal was reduced (n = 40–43 areas/3 animal each). Data are given as mean ± s.e.m.; p values were determined with student's t test. Scale bars: 200 μm (A), 5 μm (B).