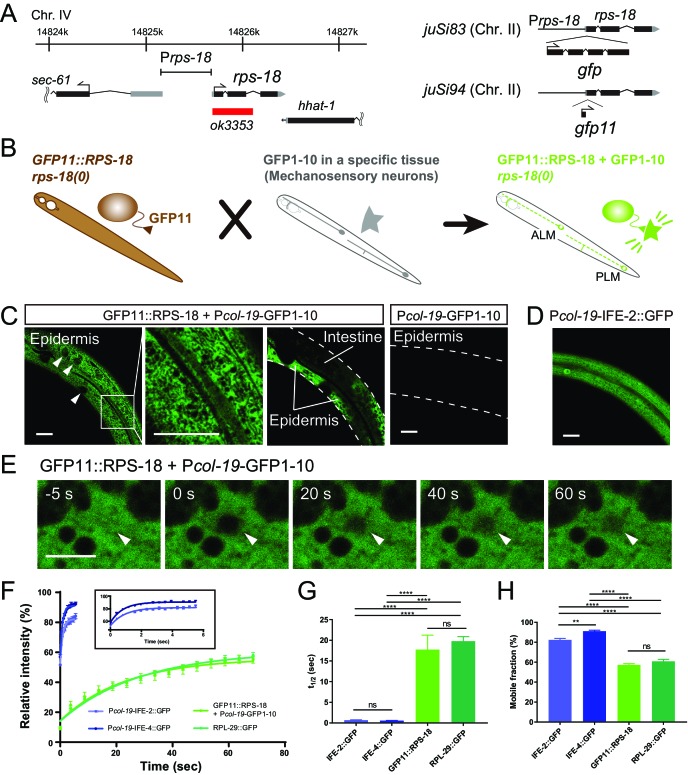
Figure 1. Ribosome Imaging Based On split GFP (RIBOS).
(A) Schematics of endogenous rps-18 locus on chromosome IV and single-copy transgenes on chromosome II. Black box: exon, Grey box: untranslated region, Red box: deletion. (B) Schematic of RIBOS for mechanosensory neurons. The rps-18 fused to the smaller part of split GFP (GFP11) is replaced to the endogenous rps-18 (juSi94[GFP11::rps-18]; rps-18(0), left). The larger part of split GFP (GFP1-10) is overexpressed using a high-copy transgene in a targeted tissue (middle). After crossing these strains, GFP1-10 binds to the GFP11::RPS-18 in the targeted tissue and visualize RPS-18 (right). (C) Epidermis-specific Pcol-19-RIBOS (juSi94[GFP11::rps-18]; rps-18(0); juEx5375[Pcol-19-GFP1-10]). The RIBOS signals were excluded from the nuclei (Left panel, arrowheads) and reticular structures (magnified image). Although GFP11::RPS-18 is expressed in the intestine, it had no signals. The negative control only expressed GFP1-10 (juEx5375) in the epidermis. Scale bars: 20 µm. (D) Diffuse IFE-2 expression visualized by juEx5809[Pcol-19-IFE-2::GFP]. (E) Representative images of the FRAP experiment using Pcol-19-RIBOS. The fluorophore was bleached in the area (arrowheads) at 0 s. Scale bars: 2 µm. (F) Fluorescent recovery after photobleaching was plotted for juEx5809[Pcol-19-IFE-2::GFP], juEx5811[Pcol-19-IFE-4::GFP], Pcol-19-RIBOS, and juSi123[RPL-29::GFP]; rpl-29(0). The line represents the one-phase fit to an exponential function for each plot. The inset shows the magnified graph for IFE-2::GFP and IFE-4::GFP. Error bars indicate S.E.M. (G and H) t1/2 and mobile fraction calculated from (F). n= 5 or 6. Error bar indicates S.E.M., Statistics: One-way ANOVA, ns: p>0.05, p**<0.01, p****<0.0001.