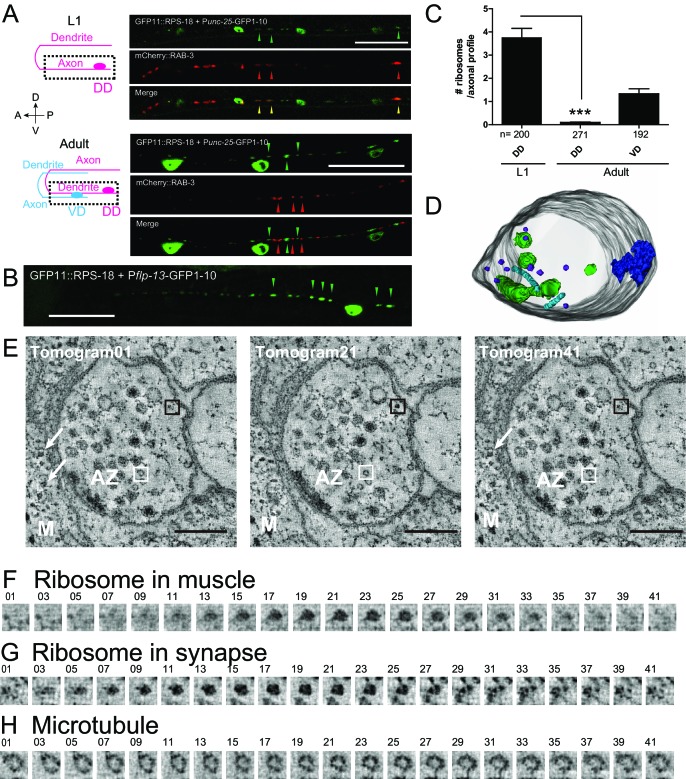
Figure 3. Ribosomes localize to the synaptic compartment in motor neurons.
(A) Schematic illustrates GABAergic motor neurons at the L1 or adult stage, in which dotted squares indicate imaged regions. As VD neurons are born, DD neurons change the innervation. GABAergic motor neuron-specific Punc-25-RIBOS (green arrowheads) and a presynaptic marker Punc-25-mCherry-RAB-3 (red arrowheads) were colocalized at the L1 stage (yellow arrowheads) but not at the adult stage. Scale bars: 20 µm. (B) DD-neuron specific Pflp-13-RIBOS showed punctate signals in the ventral cord (green arrowheads). Scale bar: 20 µm. (C) The number of ribosomes were counted in the axonal profiles of serially reconstructed electron micrographs for GABAergic motor neurons. Numbers of axonal profiles are indicated. Statistics: Student’s t-test, ***p<0.001. (D) A representative presynaptic volume reconstructed from EM tomograms of the adult motor neurons in the ventral cord, showing that presynaptic terminals contain ribosomes. Purple objects: ribosomes, blue: active zones, light blue: microtubules, green: endosomes. (E) Representative electron tomograms of presynaptic terminal of a motor neuron in the ventral nerve cord of an adult animal with 12 nm intervals. The active zone is surrounded by synaptic vesicles and dense core vesicles. White arrowheads indicate ribosomes in muscles (M). White boxes mark microtubules, which have a similar diameter as a ribosome; black boxes ribosomes. (F–H) Electron tomograms with 1.2 nm intervals for a ribosome in muscle (F), and a ribosome (G) and a microtubule (H) in the presynaptic terminal, showing that a microtubule and a ribosome have a similar diameter, but microtubule is continuous in z-direction unlike ribosome.