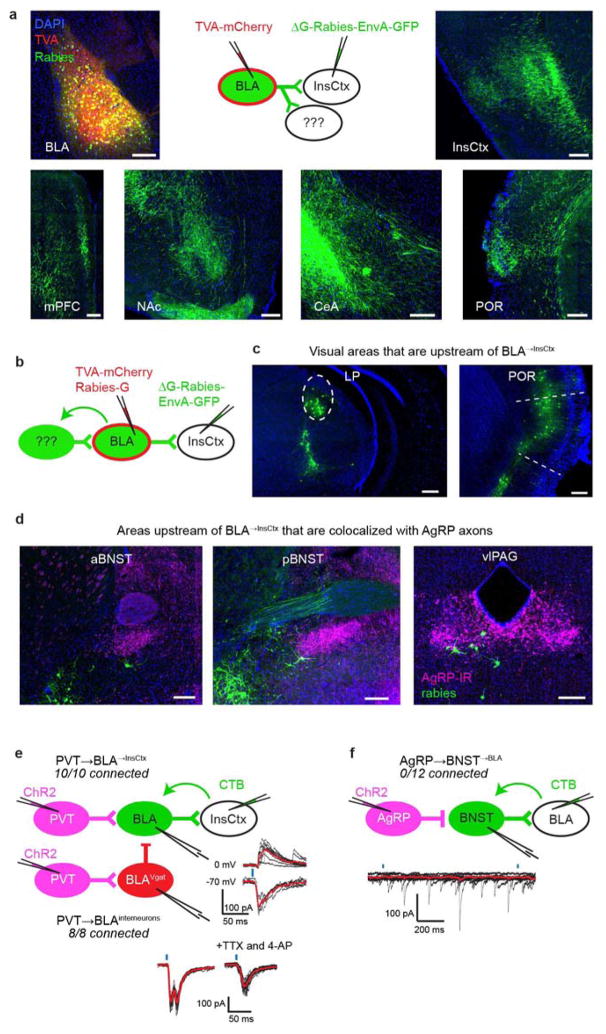
Extended Data Figure 8. Further interrogation of the pathway from AgRP neurons to InsCtx.
a, BLA→InsCtx neurons send axon collaterals to several other BLA targets. Top middle: rabies-based axon collateral mapping approach. Top left: image of the BLA (AAV-FLEX-TVA– mCherry injection site in Emx1-ires-Cre mice), containing neurons labelled with TVA–mCherry (red) and rabies (green). Top right: image of InsCtx (rabies injection site) containing axons labelled with rabies (green). Bottom: images of additional sites that also contained axons labelled with rabies after rabies injection into InsCtx. Scale bars, 200 μm. mPFC, medial prefrontal cortex. b–d, Additional inputs to BLA→InsCtx. b, Schematic of rabies-based, projection-specific monosynaptic tracing of inputs to BLA→InsCtx neurons. c, Images of visual areas containing rabies-labelled neurons (green). Scale bars, 200 μm. d, Images of additional sites containing rabies-labelled neurons (green) that anatomically co-localized with AgRP axons (magenta). vlPAG, ventrolateral periaqueductal grey; aBNST and pBNST, anterior and posterior bed nucleus of the stria terminalis, respectively. e, PVT neurons provide input to BLA→InsCtx neurons and to BLA inhibitory interneurons. Left: schematic of CRACM from PVT neurons to BLA→InsCtx neurons (labelled by CTB injection in InsCtx) or to BLA inhibitory interneurons (labelled by AAV-FLEX–mCherry injection into BLA of Vgat-ires-Cre mice). Note that all recorded neurons received input from PVT (ten out of ten BLA→InsCtx neurons, eight out of eight BLA inhibitory interneurons). Top right: light-evoked excitatory postsynaptic currents (−70 mV holding potential) and inhibitory postsynaptic currents (0 mV holding potential) in a BLA→InsCtx neuron. Note the longer latency and higher temporal jitter of the inhibitory postsynaptic currents, suggesting that they were di/polysynaptic. Bottom right: light-evoked excitatory postsynaptic currents in a BLA interneuron. Note that light-evoked currents had two peaks (monosynaptic and di/polysynaptic), and that the second peak was eliminated by bath application of tetrodotoxin (TTX) and 4-aminopyridine (4-AP), demonstrating that it was di/polysynaptic. Scale bars, 100 pA, 50 ms. f, BNST→BLA neurons did not receive monosynaptic input from AgRP neurons. Top: schematic of CRACM from AgRP neurons to BNST→BLA neurons. Bottom: example recording of AgRP inputs to a BNST→BLA neuron. Black lines are individual sweeps; red line is the average of 15 sweeps. No recorded BNST→BLA neuron received input from AgRP neurons (0 out of 12 connected).