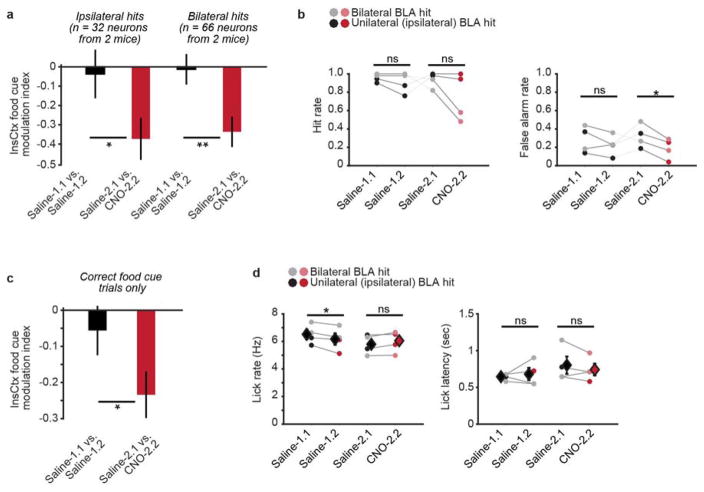
Extended Data Figure 10. Further analyses of BLA→InsCtx inhibition.
a, InsCtx food cue modulation index (in the absence versus presence of BLA→InsCtx inhibition) for mice with ipsilateral (left) and bilateral (right) BLA hits. Note overall stability on day 1 (saline versus saline) but attenuation of cue responses (resulting in a negative food cue modulation index) after CNO injection on day 2 in both groups. Values are median ± s.e. median. *P < 0.01; **P < 0.001; Mann–Whitney U-test (ipsilateral: n = 32 neurons from two mice; bilateral: n = 66 neurons from two other mice). b, Behavioural responses to the food cue (left) and to the other cues (right) during BLA→InsCtx inhibition. Each dot represents one mouse; lines connect two same-day blocks from the same mouse (two saline blocks on day 1: Saline-1.1, Saline-1.2; and a saline block followed by a CNO block on day 2: Saline-2.1, CNO-2.2). Dark dots: mice with ipsilateral (to InsCtx imaging hemisphere) hits; light dots: mice with bilateral hits. Note that behavioural responses to the food cue were reduced after BLA→InsCtx inhibition only in the two mice with bilateral hits, but that false alarm rates were reduced in all mice. *P < 0.01; NS, not significant (P > 0.2); paired t-test (n = 4 mice). c, InsCtx food cue modulation index calculated using only those trials with correct behavioural responses. Note overall stability on day 1 but attenuation of cue responses after CNO injection on day 2. Values are median ± s.e. median. *P < 0.03, Mann–Whitney U-test (n = 98 neurons from four mice). d, Lick rate (left) and lick latency (right) during BLA→InsCtx inhibition. Each dot represents one mouse; lines connect two same-day blocks from the same mouse (two saline blocks on day 1: Saline-1.1, Saline-1.2; and a saline block followed by a CNO block on day 2: Saline-2.1, CNO-2.2). Note that lick rates exhibited a small but significant decrease between Saline-1.1 and Saline-1.2 (*P = 0.04), but no significant change between Saline-2.1 and CNO-2.2 (P = 0.3). There was no significant change in lick latency (P > 0.3). NS, not significant; paired t-test (n = 4 mice).