Fig. 6.
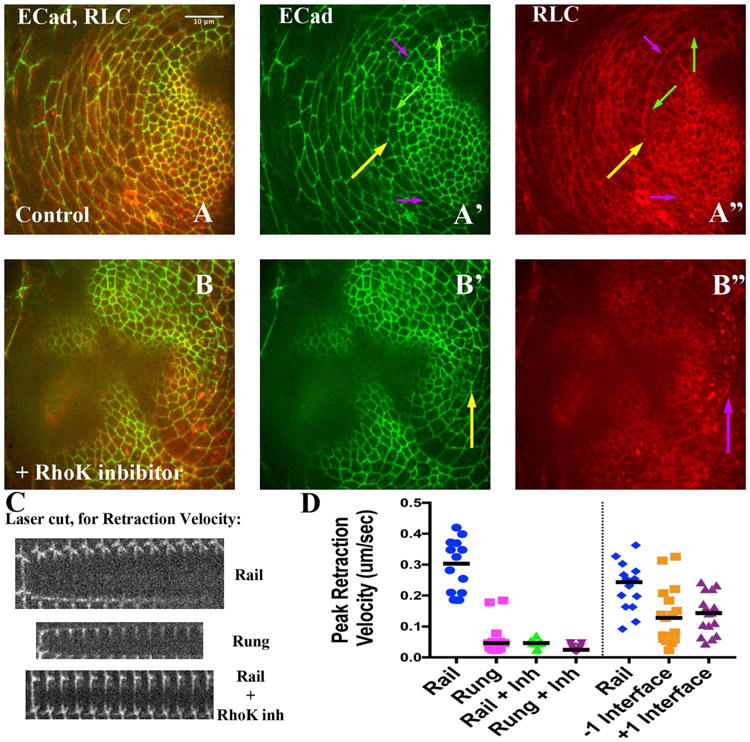
Tension along Rails is significantly decreased by Rho Kinase inhibitor treatment. A and B) Late third instar disks imaged live, expressing ECadeherin∷GFP (A′, B′, green) and RLC∷mCherry (A″ and B″, red). Yellow arrows highlight the rail. A′) The purple arrows point out example rail interfaces that would have been targeted for ablation while green arrows point out rung interfaces (see panel C, below). A″) Note relative enrichment of RLC∷mCherry along rails (purple arrows) compared to rungs (green arrows). B – B″) A different disk, about 30 min after treatment with the Rho Kinase inhibitor. B′) Yellow arrows point to a rail interface. B″) Note how area of rail interface has lost RLC∷MCherry enrichment; and instead exhibits more punctate signal. C) Three montages, from top to bottom representing three example laser ablations: a rail, a rung, and a rail interface after addition of the Rho Kinase inhibitor. In each, the first strip of the montage is before ablation, while subsequent strips are at 5-s intervals (see Section 4). D) Normalized peak reaction velocity is presented in a scatter plot. Scale bar applied to montages would be 5 μm.
