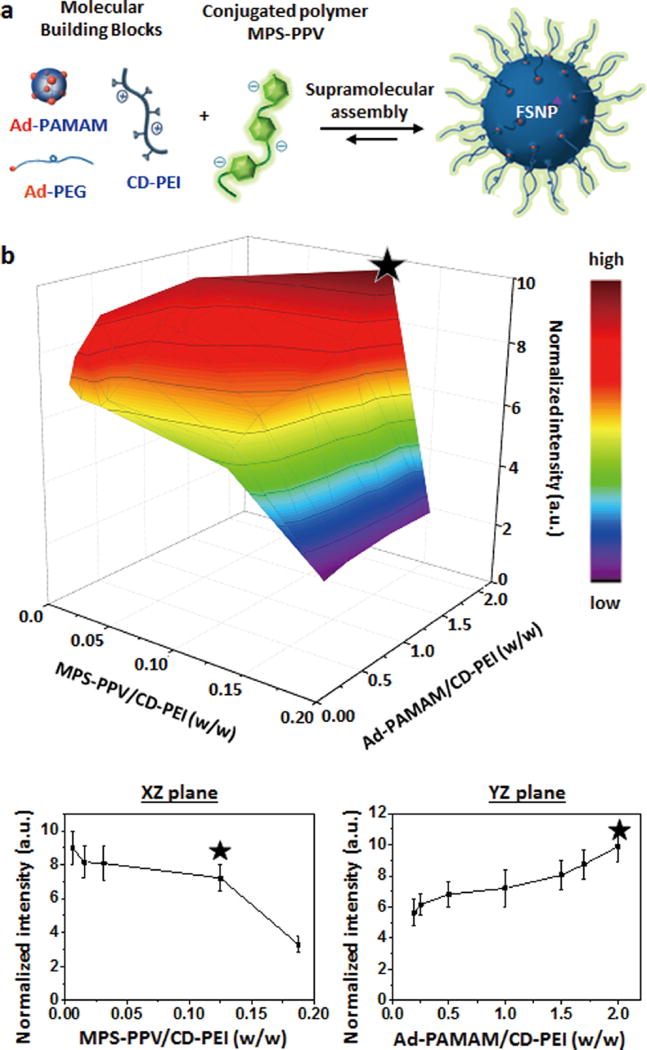
Figure 2.
(a) A small combinatorial library of FSNPs with 27 different formulations is achieved by performing supramolecular assembly of MPS-PPV and three molecular building blocks (i.e., Ad-PAMAM, Ad-PEG, and CD-PEI) in different mixing ratios. (b) Three-dimensional profile of FSNPs’ fluorescent intensities with variation (27 data points) of (i) MPS-PPV/CD-PEI ratio (w/w) and (ii) Ad-PAMAM/CD-PEI ratio (w/w). The fluorescent intensities of FSNPs are normalized to the observed intensities of free MPS-PPV of corresponding concentration for each FSNP formulation. The XZ and YZ planes across the optimal performance present the normalized fluorescent intensity variation of FSNPs depending on MPS-PPV/CD-PEI ratio (w/w) and Ad-PAMAM/CD-PEI (w/w), respectively. The FSNPs exhibiting optimal fluorescent performance (⋆) are obtained with a specific formulation of the mixing ratio among the molecular building blocks, that is, MPS-PPV/CD-PEI ratio (w/w) = 0.125:1 and Ad-PAMAM/CD-PEI ratio (w/w) =2.0:1.