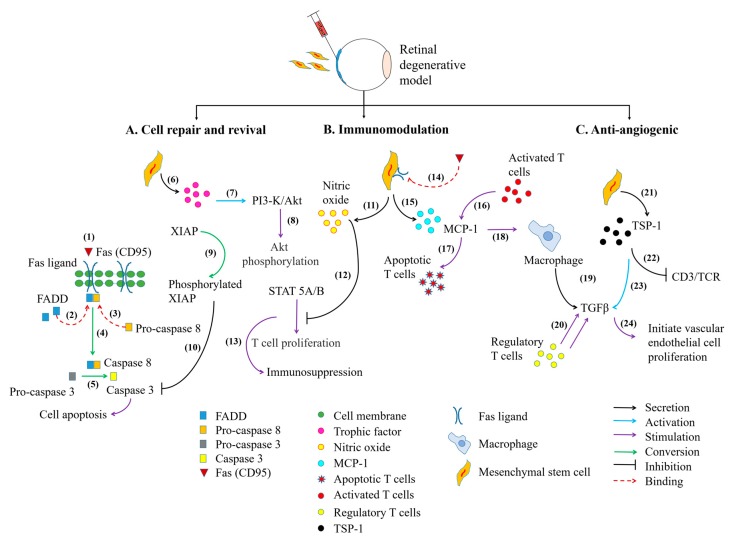
Figure 3.
The signaling pathways involved in MSC-mediated therapeutic strategies in the eye. The cell death machinery involves (1–2) the binding of Fas/Fas ligand, which assembles Fas-Associated protein with Death Domain (FADD) to form a docking site for pro-caspase 8. This event initiates the (3–4) crosslinking of pro-caspase 8 to FADD and activates caspase 8. Activated caspase 8 (5) induces the conversion of pro-caspase 3 into caspase 3 which are essential for the initiation of cell apoptosis. The MSCs cellular reparative action can be exerted (6–7) by the release of its beneficial trophic factors, including IL-6 which could further promote the migration of MSCs towards site of injury. The binding of IL-6 on MSCs will activate Phosphatidylinositol-3-Kinase (PI3-K)/Akt signaling pathway. (8–10) The phosphorylated Akt then induces X-linked Inhibitor of Apoptosis Protein (XIAP) phosphorylation leading to inhibition of caspase 3 activity. The immunomodulatory action of MSCs can be depicted through (11–13) MSCs secretion of nitric oxide, which hampers Signal Transducer Activator-of-Transcription 5 (STAT5) phosphorylation and progressively leads to attenuation of T cell proliferation. The alleviation of T cell activity can be modulated through (14–15) the expression of Fas ligand on MSC cell surface. This creates binding site for Fas protein, in which induces MSCs secretion of Monocyte Chemotactic Protein-1 (MCP-1) protein. (16–17) The secreted proteins subsequently attract and induced apoptosis of activated T cells. (18–20) Accumulation of apoptotic T cells further stimulate macrophage to release Transforming Growth Factor-beta (TGF-β) and subsequently recruit regulatory T cells. The regulatory T cells could also convert cytotoxic T cells into regulatory T cells. In addition, (21–22) MSCs also secrete Thrombospondin type-1 (TSP-1) proteins to suppress Cluster of Differentiation 3 (CD3)/T cell receptor-mediated T cell proliferation. (23–24) The released TSP-1 proteins activate TGF-β activity to initiate vascular endothelial cell remodeling. MSC cell differentiation is not mentioned in this figure.