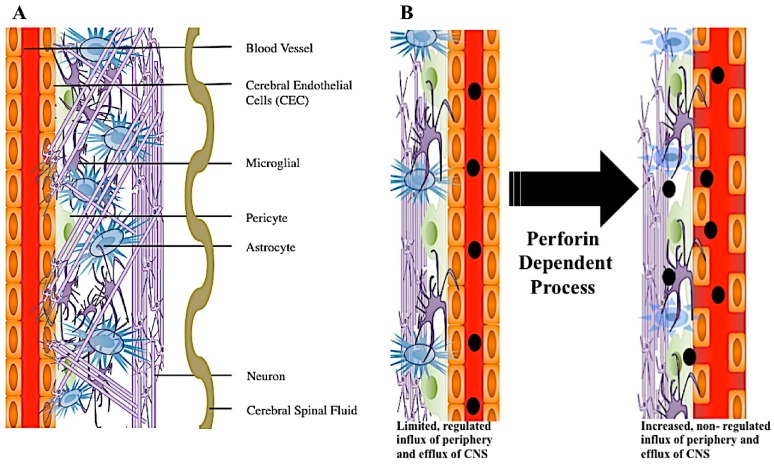
Figure 4.
2D representation of perforin mediated disruption of the blood–brain barrier. Surrounding the blood vessel is a layer of endothelial cells held together by tight junctions. Encompassing the enodthelial cell layer are various brain cells comprising the neural vascular unit (NVU). NVU cell types include pericytes, astrocytes, microglia, and neurons. Additionally, sinuses run through this dense environment carrying cerebral spinal fluid (CSF) throughout the brain (A). During neuroinflammation, the blood–brain barrier can be disrupted through a perforin dependent process. During this process, CEC tight junctions become disorganized and CNS permeability occurs. Where there was once vascular integrity and sequestration of the CNS, there is now increased non-regulated influx of molecules from the blood (B).