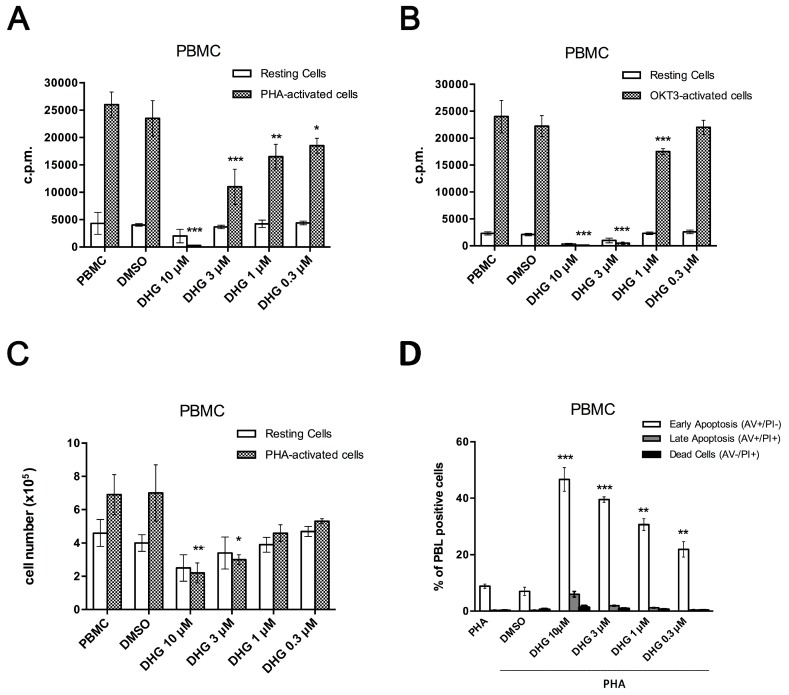
Figure 1.
9,11-Dihydrogracilin A (DHG) inhibits Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells (PBMC) proliferation and viability and induces apoptosis. (A) Unstimulated PBMC and phytohemagglutinin (PHA)-activated PBMC from healthy donors were treated with DHG at the indicated concentrations. Proliferation was measured after 18h of 3H-thymidine incorporation (1 µCi). The counts per minutes (c.p.m.) ± the SD of the triplicates of five independent experiments are shown. (ANOVA * p < 0.05, *** p < 0.001, ** p < 0.01 versus PHA-treated PBMC); (B) Unstimulated PBMC and CD3 monoclonal antibody (OKT3)-activated PBMC of healthy donors were treated with DHG at the indicated concentrations. Proliferation was measured after 18h of 3H-thymidine incorporation (1 µCi). The c.p.m. ± the SD of the triplicates of five independent experiments are shown. (ANOVA * p < 0.05, *** p < 0.001, ** p < 0.01 versus OKT3-treated PBMC); (C) Unstimulated PBMC and PHA-activated PBMC from healthy donors were treated with DHG, cultured for 6 days and stained with trypan blue. Cell viability was compared to that observed in PHA-activated PBMC (ANOVA * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01). The histogram reported show the percent of live PBMC; (D) Induction of apoptosis was measured by annexin V and propidium iodide (PI) double staining through fluorescence-activated cell sorting (FACS) analysis in DHG-treated healthy donor PBMC, after 48 h. The panel reporting representative dot plots of 4 different experiments performed with similar results is included in the supplementary section (Supplementary Figure S1). Histograms in D indicate total percentage of early (Annexin V-positive cells/PI-negative cells) and late apoptotic events (Annexin V/PI-double positive cells) as well as necrotic cells (Annexin V-negative cells/PI-positive cells). Results are representative of 4 independent experiments and expressed as mean ± SD (ANOVA, *** p < 0.001, ** p < 0.01). DMSO, dimethyl sulfoxide.