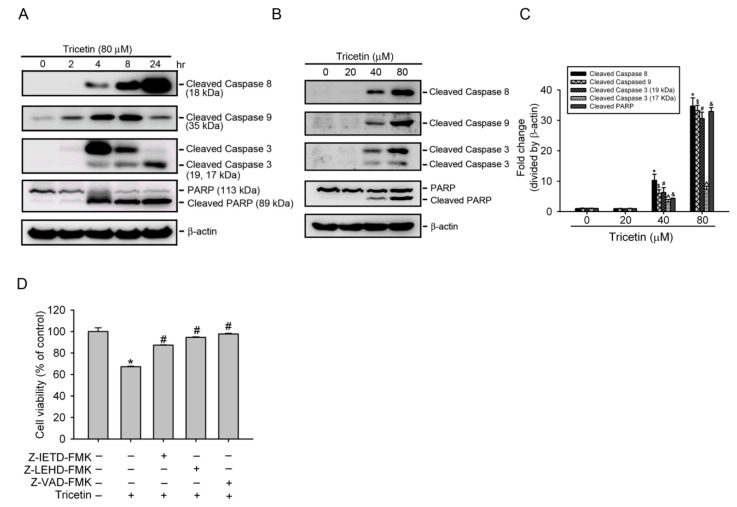
Figure 3.
Tricetin induces caspase-dependent apoptotic cell death in HL-60 cells. (A) Expression levels of cleaved caspases-3, -8, and -9, and poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) were assessed by a Western blot analysis after treatment with 80 μM tricetin for indicated time points; (B) Activated caspase-8, -9, and -3, and cleaved PARP protein expressions were upregulated in a concentration-dependent fashion after treatment of HL-60 cells with various concentrations of tricetin (0~80 μM) for 8 h; (C) Quantitative results of cleaved caspase-3, -8, and -9, and PARP protein levels, which were adjusted to the β-actin protein level and expressed as multiples of induction beyond each respective control. Values are presented as the mean ± SE of three independent experiments. *, #, &, ^, $ p < 0.05, compared to the vehicle control groups; (D) Cells were treated with 40 μM tricetin for 24 h in the presence or absence of 50 μM Z-VAD-FMK, Z-LEHD-FMK, or Z-IETD-FMK. Cell proliferation was determined by an MTS assay. Data are presented as the mean ± SE of three independent experiments performed in triplicate. * p < 0.05, control vs. tricetin; # p < 0.05, tricetin vs. Z-VAD-FMK, Z-LEHD-FMK, or Z-IETD-FMK plus tricetin.