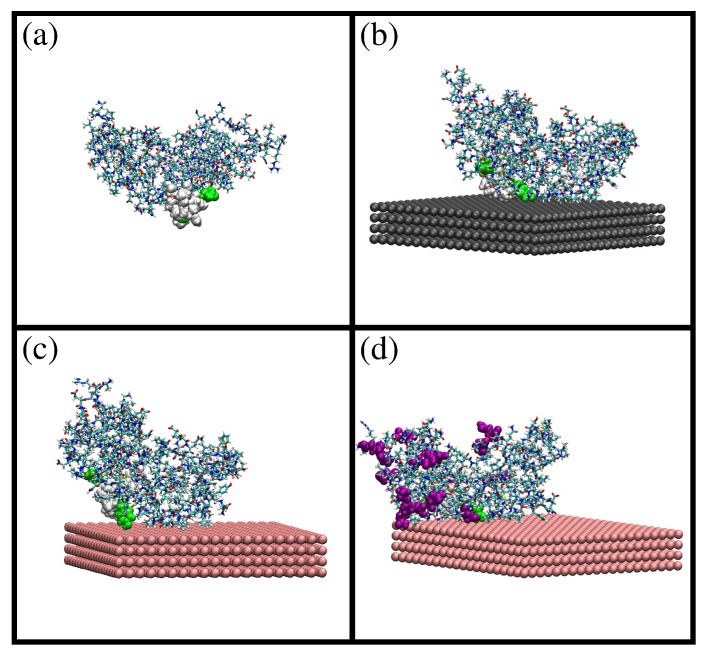
Figure 1.
Snapshots from MD simulations of -casein protein in different situations: (a) protein at pH 7 and 298 K; (b) protein at pH 7 and 298 K (charge −8e) adsorbed onto a neutral hydrophobic surface; (c) protein at pH 7 and 298 K (charge −8e) adsorbed onto a negatively-charged hydrophobic surface ( = −0.62 e/nm2); and (d) protein at pH 4 and 298 K (charge +6e) adsorbed onto a negatively-charged hydrophobic surface ( = −0.62 e/nm2). The residues 70, 73, 75–82, 85 and 126 (corresponding to the most hydrophobic region of the protein) are shown as van der Waals spheres. In (d), amino acids protonated due to the change in pH are shown as purple van der Waals spheres. These images were made with VMD [29].