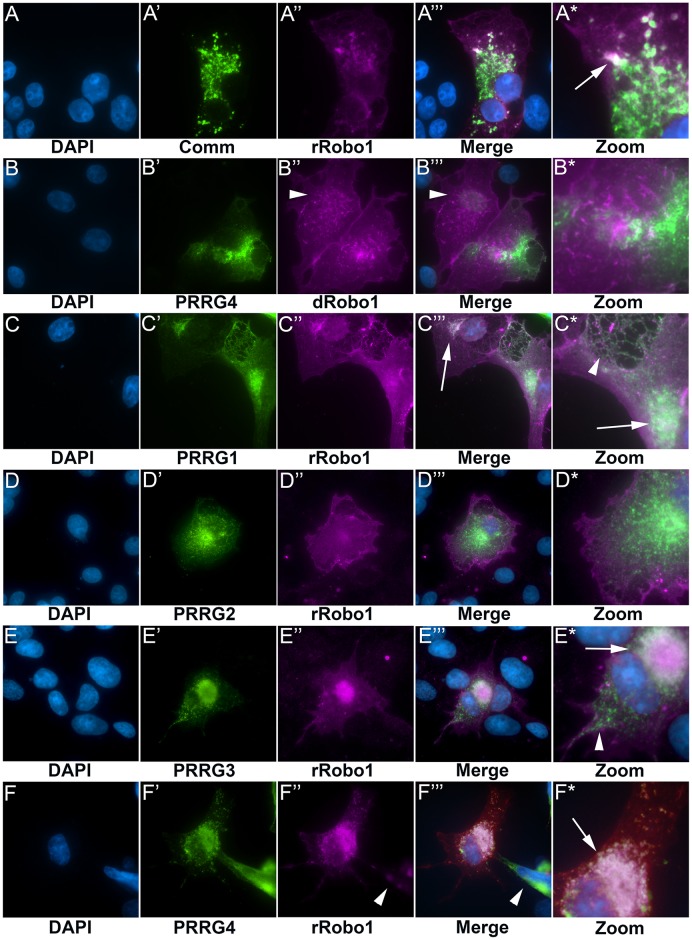
Fig 5. Co-localization of Comm, PRRG and Robo proteins.
COS cells were transfected with epitope tagged constructs as indicated under the figure panels. Protein expression was detected by antibody labeling and fluorescence microscopy. Nuclei were detected by DAPI (blue) staining. A. Cells transfected with both Comm and rRobo1. Despite the presence of significant amounts of Comm protein (green), rRobo1 remains localized at the cell surface and throughout the cell (magenta), suggesting that these proteins do not interact in this assay. There is a very limited degree of overlap of Comm and rRobo1 expression within the cell (white; arrow in A*) but also a significant lack of overlap in most other areas. B. Co-expression of both PRRG4 and dRobo1. In this image, two cells are transfected with dRobo1 (magenta), but only one cell expresses high levels of PRRG4 (green). Comparison of the two cells reveals that the pattern of dRobo1 in the cell with a low level of PRRG4 (arrowhead) shows little difference with the cell expressing PRRG4 suggesting the two proteins do not interact. Almost no overlap (white) is seen in the magnified panel (B*). C. PRRG1 and rRobo1 display a slight degree of co-localization in the presumed ER/Golgi when co-expressed (white areas, arrows in C”‘ and C*). In areas not adjacent to the nucleus, strong separation of the two proteins is seen (arrowhead in C*) suggesting they are not interacting. D. Co-expression of PRRG2 and rRobo1 leads to little or no co-localization of the proteins. E. Expression of PRRG3 can lead to a reduction of rRobo1 on the cell surface (E”) and limited co-localization around the nucleus (arrow in E*). Nevertheless, the two proteins do not co-localize in many parts of the cell (arrowhead in E*). These results suggested that PRRG3 may have a limited capacity to interact. F. Co-expression of PRRG4 and rRobo1 results in a strong reduction of cell surface rRobo1 (F”) and co-localization of the two proteins throughout the cell, particularly in the presumed ER/Golgi adjacent to the nucleus (arrow in F*). An adjacent cell expresses a high level of PRRG4 and a low level of rRobo1 (arrowheads in F” and F”‘) suggesting that PRRG4 may be resulting in degradation of rRobo1. These results strongly suggest that PRRG4 and rRobo1 interact in cell culture.