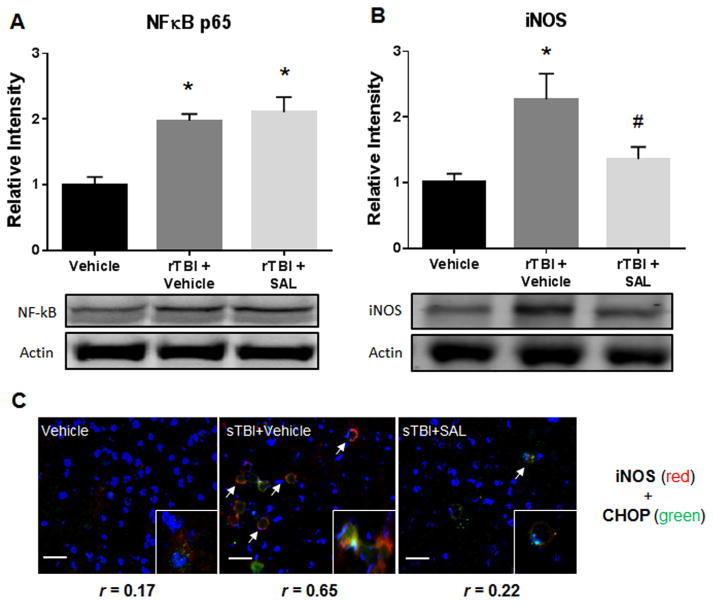
Fig. 6.
SAL reduces neuroinflammation after repetitive blast. We measured a significant increase in NFκB p65 expression at two weeks post-rTBI (*P<0.05 vs Vehicle); and when SAL was administered post-rTBI (*P<0.05 vs Vehicle) (A). We revealed a significant increase in iNOS protein expression at two weeks post-rTBI (*P <0.05 vs vehicle); SAL significantly mitigated iNOS expression (#P<0.05 vs sTBI+Vehicle) (B). One-way ANOVA, Newman-Keul’s post hoc. Mean±S.E.M. n=4. Colocalization of iNOS (red) merged with CHOP (green) was determined by levels of yellow in each image (Overlap coefficient; r values). All panels display nuclear counterstain DAPI (blue). Arrows demarcate iNOS fluorescence (C). Images are from the lateral orbitofrontal cortex. Images are displayed at 20 ×; Insets displayed at 63 ×. (Scale bars =30 μm).