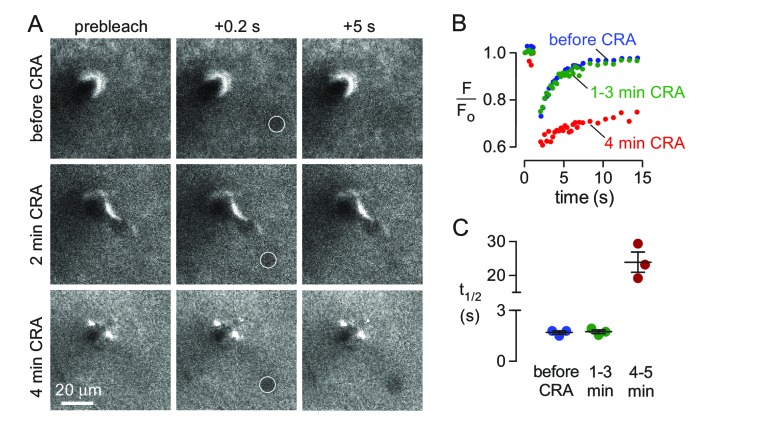
Figure 4. Effects of abrupt cessation of cardiac and respiratory pulsations on solute transport in brain parenchyma.
(A) Individual frames of a 10 μm diameter circular region (white circle) taken prior to (top panels), immediately following (middle panels) and 4 min after (bottom panels) cardiorespiratory arrest. (B) Fluorescence recovery curves for experiments as in A showing average of 2–3 trials done before (basal), at 1–3 min, or at 4–5 min following cardiorespiratory arrest. (C) Summary of fluorescence recovery half-times (t1/2) before and following cardiopulmonary arrest (mean ± S.E.M., 3 mice). Recovery half-time was not significantly different between baseline and 1–3 min. following cardiorespiratory arrest by t-test (p=0.78).