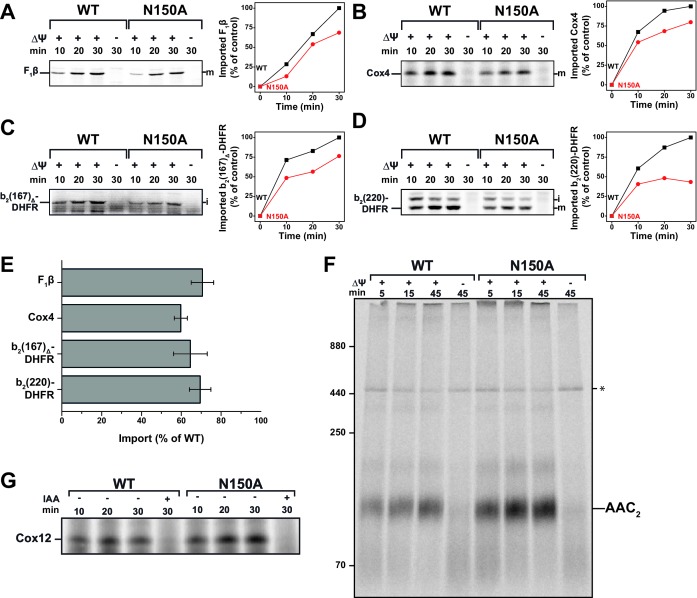
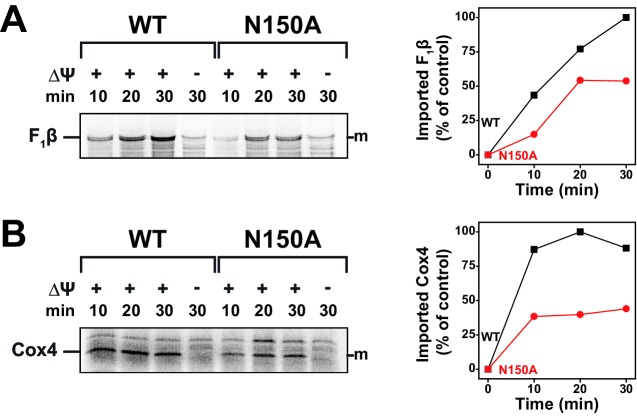
Figure 4. Tim23N150A exhibits significant import defects for various TIM23 substrates.
(A–D) Import capability of wild type and tim23N150A mutant mitochondria was determined by incubating [35S]-radiolabeled matrix destined precursors F1β (A), Cox4 (B), b2(167)Δ-DHFR (C) or the inner membrane sorted b2(220)-DHFR (D) with isolated mitochondria for 10, 20 or 30 min. The import reactions were stopped by dissipating ΔΨ and subsequent Proteinase K (PK)-digest. Digital autoradiographs (left) were analyzed and quantified (right). Maximum import into wild type mitochondria was set to 100%. (E) Relative import efficiency after 15 min of import into mitochondria containing Tim23N150A was quantified for different substrates. Error bars represent standard error of the mean (SEM, n = 3). (F) Carrier import into Tim23N150A-containing mitochondria was assessed via ADP/ATP carrier (AAC) complex assembly by incubating [35S]-radiolabeled AAC with isolated mitochondria for 15, 30 or 45 min. The import reaction was stopped by dissipating ΔΨ and subsequent PK-digest. Assembly of AAC dimer was monitored by BN-PAGE. (G) The MIA substrate Cox12 was [35S]-radiolabeled and imported into Tim23N150A-containing mitochondria for 10, 20 or 30 min. The import reaction was stopped by addition of iodoacetamide (IAA) and subsequent PK-digest.