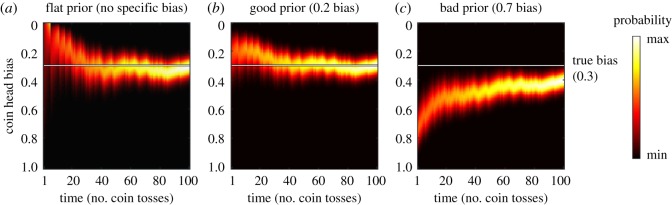
Figure 7.
Bayesian updating. We are presented with a biased coin that gives heads on 30% of tosses. Each heat map shows how our posterior (colours) over hypotheses about coin bias (vertical axis) evolves as we observe more and more coin tosses (horizontal axis). The white line indicates the true value. The prior at a given point in time is the posterior from the previous point in time. The prior for time 1 was set to be (a) flat across hypothesis, (b) centred on the truth or (c) centred on a wrong value.