Table 2.
Comparison between the three groups of renal damage evolution concerning clinical parameters at the index UTI, number of recurrent UTI, presence of duplex, renal damage at the index DSMA scan, and status of vesicoureteral reflux
| Progression (n = 20) | Regression (n = 20) | Unchanged (n = 63) | p value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gender, boys n (%) | 10 (50%) | 9 (45%) | 27 (43%) | 0.75 |
| Index UTI | ||||
| Age, months median (range) | 5.5 (1.3–16.0) | 4.6 (0.5–22.0) | 6.5 (0.3–21.4) | 0.70 |
| CRP, highest, mg/median (range) | 135 (23–430) | 110 (5–210) | 120 (5–300) | 0.32 |
| Bacterial species | ||||
| E.coli, n (%) | 12 (60%) | 18 (90%) | 55 (87%) | 0.013 |
| Non-E.coli sp. | 8 | 2 | 8 | |
| Recurrent febrile UTI, n (%) | 13 (65%) | 2 (10%) | 19 (30%) | <0.001 |
| Renal damage at index DMSA scan, n (%) | ||||
| Minor | 5 (25%) | 11 (55%) | 37 (59%) |
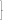 0.048 0.048 |
| Moderate | 9 (45%) | 7 (35%) | 11 (17%) | |
| Pronounced | 6 (30%) | 2 (10%) | 15 (24%) | |
| VUR, n (%) | ||||
| no VUR | 1 (5%) | 14 (70%) | 23 (37%) |
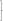 <0.001 <0.001 |
| VUR grade I to II | 3 (15%) | 2 (10%) | 9 (14%) | |
| VUR grade III to V | 16 (80%) | 3 (15%) | 29 (46%) | |
| VCUG not done | 1 | 2 | ||
UTI urinary tract infection, CRP C-reactive protein, sp. species, DMSA dimercaptosuccinic acid, VUR vesicoureteral reflux, VCUG voiding cystourethrography
